TAKE NOTE (Insights and Emerging Technology)

Digital transformation and the ability to adapt quickly are critical in today’s business environment. That’s why a growing number of companies are adopting process mining, a family of techniques that support the analysis of operational processes of event logs, with the goal of turning event data into insights and actions. In a recent Deloitte survey, 63% of organizations have already started to implement process mining, and 83% of companies are already using process mining to expand their initiatives.
Low-code automation platform Appian recently announced it has acquired process mining company Lana Labs for an undisclosed amount. Appian says that with the addition of Lana, it will be able to deliver actionable and continuous process optimization with people, systems, and data in the same workflow.
Berlin, Germany-based Lana, which was founded in 2016 by Karina Buschsieweke, Rami-Habib Eid-Sabbagh, and Thomas Baier, automates the analysis of repetitive business workflows. The container-based platform, which is portable between Amazon Web Services (AWS) Cloud and customer-managed environments, ships with pretrained algorithms for data transformation and automation.
Research firm Gartner estimates the market for hyperautomation-enabling technologies will reach $596 billion in 2022, up nearly 24% from the $481.6 billion in 2020. For example, the robotic process automation (RPA) market is expected to reach $12 billion by 2023. As organizations look for ways to accelerate the digitization and structuring of data and content, technologies like document ingestion and natural language processing will remain in high demand.
Appian CEO Matt Calkins sees a “natural synergy” between process mining, process modeling, and automation. Combining Lana process mining with Appian, he believes, will enable “rapid automation” of analysis insights for organizations’ back-office workflows. “We believe that our acquisition of Lana means that only Appian will be able to take customers from knowing to doing, in a unified suite,” he said in a statement.
Appian was founded in 1999 by Michael Beckley, Robert Kramer, Marc Wilson, and Matthew Calkins. The cloud computing and enterprise software company, which is headquartered in McLean, Virginia and has raised tens of millions in venture capital, sells a platform-as-a-service for building enterprise software apps. It’s focused on low-code development, business process management, and case management markets.
Interested in learning more about RPA? Download our FREE White Paper on “Embracing the Future of Work”
UNDER DEVELOPMENT (Insights for Developers)
COMPOSABLE ERP: WHAT IT IS AND WHY IT’S IMPORTANT PART 2

Intro
The future state of ERP will be defined by integrated applications that can be composed and recomposed to deliver customer-defined business capabilities and outcomes. Composable ERP is an agile technology strategy that can adapt and enables the foundational, administrative and operational digital capabilities enabling an enterprise to keep up with the pace of change. This type of strategy delivers a core of composable applications and, as a service, software platforms that are configurable, integrated and flexible to meet future modern technology innovations.
Wow, that was a mouthful. Lets look at how we meet the changing business needs today in our ERP system. Today we allow customization within the ERP applications to meet the demands of the business; working within a proprietary technology stack of the “monolithic approach” that ERP vendors deliver. The ERP black box adheres to proprietary, static data models, development/integration tools and business logic. The result are systems that lack agility and are unable to adapt in the face of change. The Covid-19 Crisis is a perfect example. Consider that 84% of companies have changed their operations to remain relevant in the disruption caused by the pandemic.
Wait a minute…. I can hear you saying well this isn’t that different than the Postmodern blog from last month. Well you are right there is a baseline here, but you will see that Composable ERP take the Postmodern strategy to the cloud with SaaS, and PaaS, and Data fabrics, the final frontier that ties us to our ERP vendor by exploding the concept of a static Data model.
Ok, let dig deeper…
COMPOSABLE ERP HOW DID WE GET HERE?
Here is a diagram of the changes to the ERP landscape through the years.
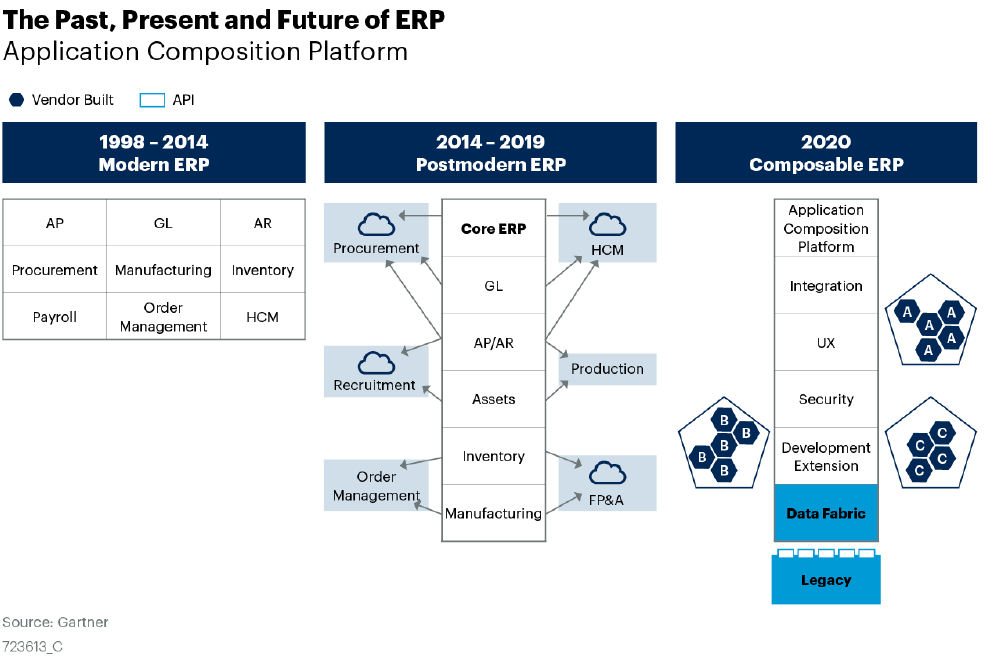
The current ERP landscape is centered around the ERP vendor product with integration. The gaps in ERP solutions are filled haphazardly, and migration plans only emphasize moving to the cloud. Nevertheless, a true transformation of the ERP landscape should focus on long-term value for your enterprise. To do this, application leaders should prepare for composable ERP with a shift to customer focus from vendor focus.
THE COMPOSABLE ERP STRATEGY
ERP is a strategy, not a product, as such, the ERP strategy requires constant engagement review and innovation. A crucial part of this strategy is the understanding that you are not at at the mercy of any vendor, and the set of technical internal (or third-party system integrator) resources that have been used to date. Remember, initially ERP is primarily and essentially a strategy for aligning the application portfolio to business objectives. Gone are the days where organizations could put ERP solutions in place and “not worry” about them until the next upgrade in five to seven years.
Composite architecture is one of the emerging trends predicted to drive technological innovation in the next 5-10years. This is an innovation that is agile by design, enabling quick adaptation to business environment changes. Composite architecture forms the foundation of composable ERP.
– Dig Deeper –
What is Process Mining
Q&A (Post your questions and get the answers you need)

Q. I am part of a team that is converting from ECC to S/4 HANA. Is there an easy way to see what transactions are obsolete in S/4?
A. Many transactions have been deprecated in SAP S/4HANA from ERP6.0. In fact, there are too many obsolete transactions in S4HANA to list. One of the frustrations is that SAP does not really provide an easy way of identifying these obsolete tcodes. I’ll show you how you can find these deprecated transaction codes quickly using SE16N
If you are undergoing a conversion from ERP6.0 to S/4HANA, then I assume you have access to your originating ERP6.0 system, or you have access to the below information from your basis team.
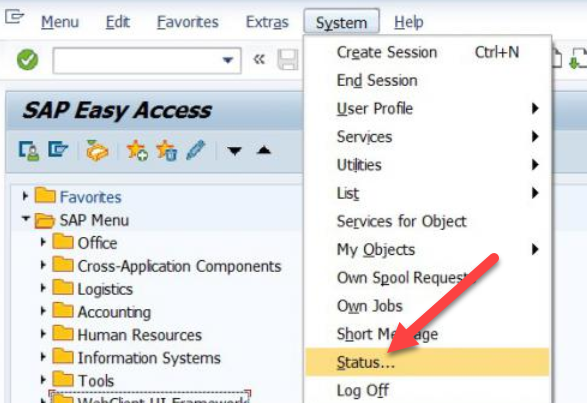
First of all, you will need to know the SAP Netweaver release of your ERP6.0 system. To find this, follow these steps:
(1) From your SAP GUI, select System>Status as below:
(2) Click the “Details” button.
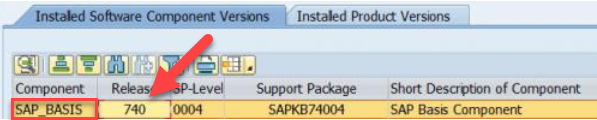
(3) Find your SAP_BASIS component, and the Release number will be next to that. So in the below example, my release is 740.
(4) Now go into your S/4HANA system via the SAP GUI and enter transaction SE16N and select table PRGN_CORR2. In the SAP Release field, enter “greater than or equal to” the release number of your ERP6.0 system, as below:
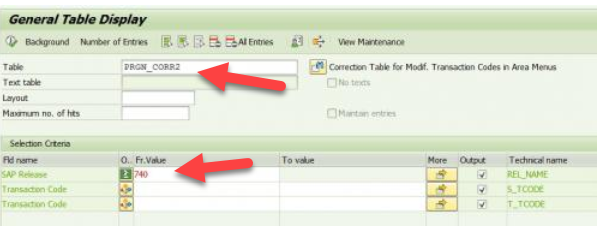
This list now gives you the old SAP transaction codes and the new ones they are replaced with – see below.
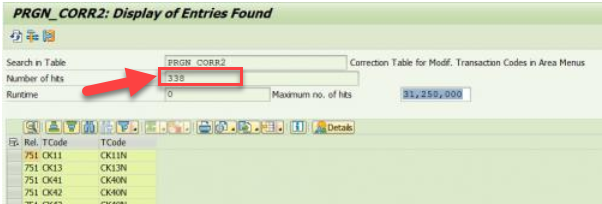
So for my example, 338 transactions have been deprecated from my ERP6.0 system to my S/4HANA system. Please be aware, that this does not necessarily mean that the transactions are no longer available – some of them are still there.
Do not forget to read the SAP Simplification list for the latest version of S/4HANA. Here is a link to the 1909 simplification list.
Cheers!



