Solving The legacy Conundrum With iBPMs
TAKE NOTE (Insights into Emerging Technology)

When companies want to implement technologies of the digital age, and access leading-edge capabilities – such as skills-based routing and tracking, native mobile access, social collaboration, robotic process automation and predictive analytics – they have to accommodate the legacy applications somehow, or risk losing what they contain.
The question is how to adapt the legacy applications in order to facilitate the adoption of new applications and technologies without losing the intellectual property refined over many years and embedded in the legacy applications
Top-Down Approach with BPM
BPM offers a solution because it is a top-down approach that allows legacy applications to be modernized holistically and using iterative prototyping. From translating business objectives, goals and capabilities to enabling services-oriented architecture through to process-driven workflow and execution, BPM is a smart way of redeveloping and managing legacy applications. It allows the business to collaborate with IT in defining the processes that will govern the use of the legacy functions by abstracting the business process from the underlying code, and allowing loose coupling with other aspects of the legacy code.
BPM is a smart way of redeveloping and managing legacy applications. BPM reduces risk because it fosters an incremental, iterative approach rather than a big-bang one.
BPM thus also enables process automation by facilitating process redesign, minimizing human intervention by means of rule-based exception handling. BPM can help companies identify human interface requirements and automate exception handling through intelligent routing, tracking and task assignment. Whether the legacy application runs a transactional process or is event-driven, BPM can simplify the architecture of it by encapsulating legacy functions into services. This provides a standard interface and easy access for new requirements, plus re-use of a well-defined library of services.
And, because BPM enables ongoing monitoring and optimization, it supports continuous process improvement, driving down costs and reducing inefficiencies. Furthermore, it also enables agility by assisting the business to respond to change through rapid prototyping, development and deployment
BPM makes it possible for companies to integrate legacy applications into next-generation systems, preserving intellectual capital while enabling process automation. It has a crucial role to play in the effective digital transformation of existing businesses.
Attaining business agility is beyond fast App development and delivery. It means IT and LOB working in collaboration. Software development and operations need to go to hand-in-hand, let IT Partners connect them for you.
UNDER DEVELOPMENT (Information for Developers)
An In Depth Look At Qlik Sense Desktop – Part #2
Now that you know the basics of creating an Qlik Sense Desktop App from scratch, which we learned from Part#1 of this blog series, let’s make a new Qlik Sense App from a data file. For this demo, you can download the Qlik sample data (gettingstarteddata.xls) from Qlik here.
First, lets create a New Qlik Sense App and name it “Getting Started with Sales”.
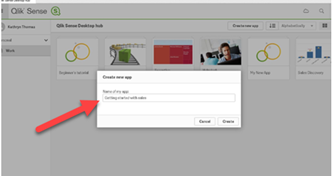
The next step is to connect to the data you want to use for your Qlik app. You can choose from any data file on your computer or your network including Microsoft Excel, Microsoft SQL, MySQL, ODBC, SAP HANA, Oracle, and web files. Or you can link to one of the data files in the Qlik Data Market. This time we will add data from a file rather than the Qlik Market
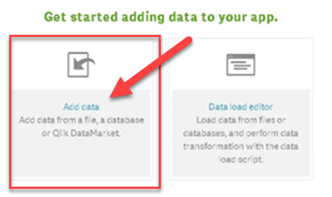
The sample data is in the Excel file you downloaded, but please note that you have many options. lets drag and drop the Excel file into Qlik. (You can also navigate to the file through Qlik).
Q&A (Post your questions and get the answers you need)

Q. I have been hearing a lot about RPA technology. Can you explain please what this is? How do you work in it, is there a methodology? Whats the big deal?
A. RPA – Robotic Process automation is a kind of automation where a machine performs human’s task in completing rules based jobs.
There are benefits to using RPA, for instance since bots are dealing with the execution here, a greater measure of work can be done in a relatively much shorter period. A faster delivery, coupled with accuracy. And since it is a safe, non-invasive technology that doesn’t interfere with the inherent systems and provides impeccable consistency in performing the activities, I would say consistency is a benefit as well.
A big benefit in my opinion would be the cost savings. It has been projected that using robotics cuts operational costs, Robots can operate 24*7 and take no leave, when compared to humans.
As far as a methodology, take a look at this:
Phases of RPA Life Cycle:
- Analysis: The first phase in RPA begins with analysis. Business team and RPA Architect work together to understand a business process for RPA development.
- Bot Development: RPA developer (Team) starts working on the requirement in their environment possibly a distinct development environment.
- Testing: Some companies conduct Testing by Separate Testing Team, while some have a dedicated testing team which performs a dedicated QA like normal SDLC flow. Best Practice is to have a dedicated testing team which performs QA of developed bot.
- Deployment and Maintenance: After the Development and Testing phases, a bot is ready for distribution and enters maintenance phase.
Please keep the following in mind….
RPA surely improves efficiency by powering repetitive human effort, but there are limitations to the types of work that it can be applied to – especially ones that require judgment
RPA is not a cognitive computing solution. It cannot learn from experience and therefore has a ‘shelf life’.
Implementing RPA to a broken and incompetent process will not fix it. RPA is not a Business Process Management solution and does not bring an end-to-end process view like a BPM suite from Pega or Appian.



