TAKE NOTE (Insights and Emerging Technology)

|
Interested in learning more about RPA? Download our FREE White Paper on “Embracing the Future of Work”
UNDER DEVELOPMENT (Insights for Developers)
Understanding Generative AI With SAP
Intro
Generative AI has made significant strides over the past few years, evolving from theoretical research into practical applications that are now revolutionizing business processes. By incorporating AI-driven technologies into its solutions, Generative AI with SAP offers enterprises the ability to automate tasks, generate insights, and enhance decision-making in ways that were unimaginable just a few years ago.
How does SAP integrate generative AI into its platforms, and what value does it bring to modern enterprises? In SAP terms, seamlessly connecting generative AI to the existing functionalities of SAP S/4HANA adds an additional enterprise dimension to AI. This helps data to effortlessly flow between multiple business processes in an enterprise.
Now let’s look at generative AI in more depth
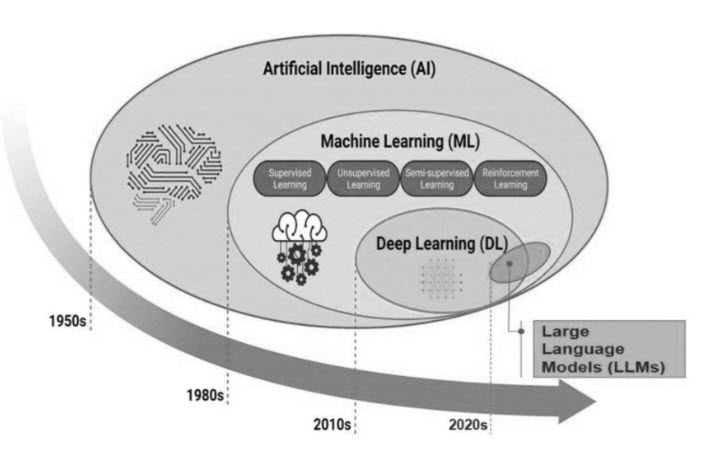
Understanding Generative AI
– Dig Deeper –
SAP’s Generative AI Transforming UX
Q&A (Post your questions and get the answers you need)

Q. How Gen AI can Change SAP S/4HANA Testing and QA?
A. As you begin your S/4HANA journey, harnessing automation, AI, and machine learning (ML) capabilities has become imperative for successful program deployment and competitive advantage. Gen AI provides a clear edge in testing and quality engineering (QE), optimizing various processes. Addressing QA challenges early in the SAP S/4HANA journey is crucial to mitigate any impact on program timelines and costs while ensuring production quality and stability.
Generative AI (Gen AI), an artificial intelligence (AI) approach that generates new data using statistical models, can revolutionize testing by automating various tasks and optimizing efficiency. Versatile models, such as GPT-3, offer unique capabilities in SAP quality engineering, reshaping the testing landscape for SAP S/4HANA programs and integrated applications.
Before going into the applications of generative AI, it helps to understand the challenges involved in SAP S/4HANA program testing. These include:
- Complexity: Testing complex integrations across legacy and 3rd party applications and critical business processes, as well as ensuring system resilience and scalability. Critical business impact with higher personas to be validated ensuring compliance, data privacy, accessibility of the systems.
- Resource-intensiveness: Acute shortage of skilled SAP consultants, and the tedious process of handling business-dependent test data
- High costs: Accumulating massive and redundant test cases repository across markets (global, regional and local) and increased cost of tools and automation
- Time and schedule: Ensuring comprehensive test coverage across BPMLs and gaps (WRICEF) within scheduled testing windows. Dealing with the unavailability of interfacing applications during testing timelines and cascading effects cause program risk on quality and timelines
OK, enough of the challenges, what can Gen AI do for S/4 HANA Testing and QA?
Automated Test Case Generation
One of the most promising applications of Gen AI in SAP S/4HANA testing is the automated generation of test cases for various business processes, including interfaces and connected systems. Traditionally, test case generation has been time-consuming and error prone. Gen AI can automate this process, producing comprehensive and accurate test cases in a fraction of that time.
SAP Signavio produces business process models as output from process discovery or design (BPMN 2.0/XML/Visio etc.) which feeds into the Gen AI to generate detailed level test cases/steps across SAP GUI or Fiori screens. The same output across business processes (Order to cash, Procure to Pay, Record to report, Plan to Produce etc.) can be converted to various automation scripts in Python, VB, Java or even RPA scripts in a matter of few minutes which would have taken substantial hours/days if performed manually.
Automated Test Data Mining
Another potential application of generative AI for SAP S/4HANA testing is the generation of test data for various combination and process variants. Generative AI can create realistic test data that mimics real-world data or even mine the test data from various SAP tables using its powerful SQVI query search. This can help to ensure that SAP S/4HANA is tested under a variety of conditions, data, and process variants to ensure highest coverage, reduced cycle time and enhanced productivity for multi country/market rollouts.
Other Gen AI Use Cases for SAP S/4HANA testing
Let us take a look at some specific examples showcasing how enterprises can harness the power of Gen AI for SAP S/4HANA testing and validation:
- Test case generation: Generating comprehensive test cases covering a wide range of business processes and scenarios from process models (Signavio, Celonis, Aris etc.)
- Test data mining: Mining test data from multiple SAP tables to find the right SAP master or transactional datasets for test case requirements
- Volume test data creation: Creating volume test data with different processes, data, and local tax variants, ensuring complete coverage for global markets
- Defect identification and prevention: Identifying and preventing defects by analyzing past incidents and root causes
- Automation and script generation: Generating automation scripts for SAP business processes and test scenarios, amplifying existing test automation solutions
- Validation and impact assessment: Assisting in validation of forms, invoices, and data accuracy, comparing textual alignments, and assessing impact of upgrades and releases on production quality and process coverage
- Automatic maintenance of test cases and automation scripts based on production changes or process changes in SAP
In the end, despite its great potential, Gen AI requires extensive training and validation due to its limitations in accuracy. The complexity of SAP and non-SAP applications may hinder AI’s applicability for end-to-end coverage.
More than likely individual AI assisted use cases will get embraced in the program and operation lifecycle, but Gen AI needs more advancement and research to cover overall enterprise landscape and business processes related use cases.
Cheers!