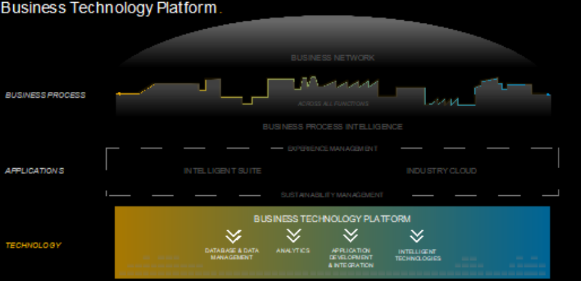
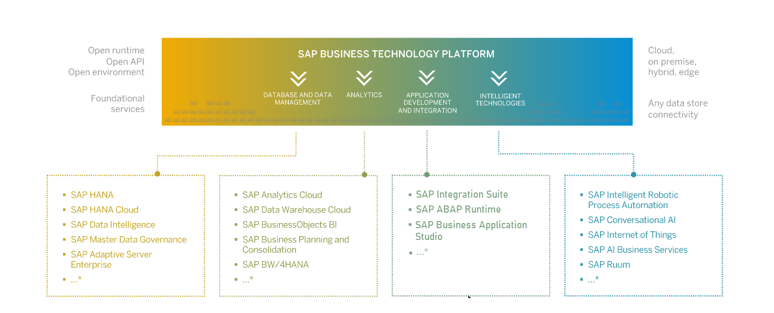
To explain how it all comes together, we will use this blog to understand the BTP, the account model it utilizes, and how to manage BTP options, services, and environments using the BTP Cockpit.
ABAP for HANA
The Extension Suite is a strategic approach for extending your cloud, on-premise, non-SAP, and SAP business solutions beyond what your core system provides.
SAP Extension Suite gives you the services, tools and capabilities to build and maintain extensions to your business apps in the cloud. Use it when you need to implement additional processes on top of your existing SAP applications.
The Business Technology Platform, or BTP for short, is a cloud-based PaaS (Platform as a Service) offered by SAP. The BTP provides application developers with a canvas where they can create applications and extensions to suit their customers customization needs.
AMDPs provide powerful abstractions that enable ABAP developers to combine the benefits of the high-speed in-memory execution of SAP HANA with the well-established ABAP runtime and lifecycle model. Along with CDS Views, CDS Table Functions, and OPEN SQL, allow ABAP developers to renovate their existing assets and create new and innovative applications for SAP Business Suite on SAP HANA without losing the platform-independence of ABAP.
Core Data Services, or CDS, is a “semantically rich” Data Definition Language (or DDL) created by SAP. It provides an easy to understand and reusable tool that ABAP developers can utilize to execute the “code pushdown” paradigm. CDS has evolved into different variants, but the ABAP developer should chiefly be concerned with two specific ones…The lesser used option is HANA CDS, the database language that can be used to create tables, views, and structures on the HANA database itself. Views created in HANA can be consumed from the Netweaver AS using Native SQL. The second and most important variant of CDS that should concern ABAPers is the ABAP CDS. While significant differences have evolved between the two variants — for example, SAP HANA-based CDS obviously operates on SAP HANA, while ABAP-based CDS operates on most major database platforms as well as SAP HANA, and each has a different type of repository for development objects — both variants pursue the same goal: to represent central data definitions as a common basis for application development of all kinds.
Chances are that if you work with SAP ABAP, you have heard of SAP HANA by now. You’ve probably heard that it’s “the future” and a “game changer.”
As time has gone by, more and more commands and constructs have been added to the ABAP language. While many changes came as a result of the introduction of SAP NetWeaver 7.02, that is nothing compared to the deluge of change that came with version 7.4. Inline ABAP DATA declarations are a new concept introduced in release 7.4 which allows you to declare your internal table variables or work areas within the code that uses them. This is done simply by adding the DATA(wa_data) or @DATA(it_data) statements.
As time has gone by, more and more commands and constructs have been added to the ABAP language. While nothing has been taken away, this is to ensure backward compatibility, the rate of change seems to be accelerating. While many changes came as a result of the introduction of SAP NetWeaver 7.02, that is nothing compared to the deluge of change that came with version 7.4.