TAKE NOTE (Insights and Emerging Technology)

Federal officials who oversee millions of active security clearances said they will relax the rules that trigger security reviews for people who face financial hardships.
The change aims to reduce the hardships resulting from layoffs, furloughs and other economic disruptions caused by shutdowns now affecting most of the country.
Specifically, the policy calls for security clearance reviews to take a broad interpretation of the “mitigation factors” that provide special consideration for people whose “financial problems were largely beyond the person’s control (e.g. loss of employment, a business downturn, unexpected medical emergency, a death, divorce or separation, clear victimization by predatory lending practices or identify theft)”.
Traditionally, security clearance reviews have frowned on debt and personal financial problems as a risk factor because it can increase an individual’s susceptibility to bribes or blackmail or increase the risk of being coerced into espionage.
Thorough reviews for security clearances are conducted every five years for those with Top Secret clearances. Reviews can also be triggered at any time if overseers identify new risk factors such as missing credit card payments, missing child support payments, getting sued or involvement with the criminal justice system. The precise factors that can trigger a review are classified.
The revised guidance for security clearance reviews comes after a request from Sen. Mark Warner, a Democrat from Virginia, who feared that people could risk losing their positions if they heed the advice of health professionals and subsequently lose out on a paycheck in order to self-quarantine.
“I write to ask you to issue guidance directing agencies to exercise appropriate leniency in considering how the coronavirus (COVID-19) may be negatively impacting adjudications for a security clearance or determination of trust,” Warner wrote on March 11.
Read More
Interested in learning more about RPA? Download our FREE White Paper on “Embracing the Future of Work”
UNDER DEVELOPMENT (Insights for Developers)
THE EVOLUTION OF EXTENDED WAREHOUSE MANAGEMENT (EWM)

Extended Warehouse Management (EWM) offers, flexible, automated support for processing various goods movements and for managing stocks warehouse complex. The system supports planned and efficient processing of all logistics processes in your warehouse.
If you currently manage your warehouse stocks using the application component Inventory Management (MM-IM), then you manage material stock based on quantity and value in several storage locations.
In contrast, EWM gives you the option of mapping your entire warehouse complex in detail in the system, down to storage bin level. Not only do you gain an overview of the entire quantity of a material in the warehouse, you can also always determine exactly where a certain material currently is in your warehouse complex. With EWM, you can optimize the use of various storage bins and stock movements and can store together material stocks from several plants in random storage areas. Using EWM, you can control and optimize processes in the warehouse.
Extended Warehouse Management is completely integrated into Inventory Management and Delivery Processing. Business processes, which you trigger in other application components, lead to physical goods movements in your warehouse. You organize, control, and monitor these goods movements using EWM.
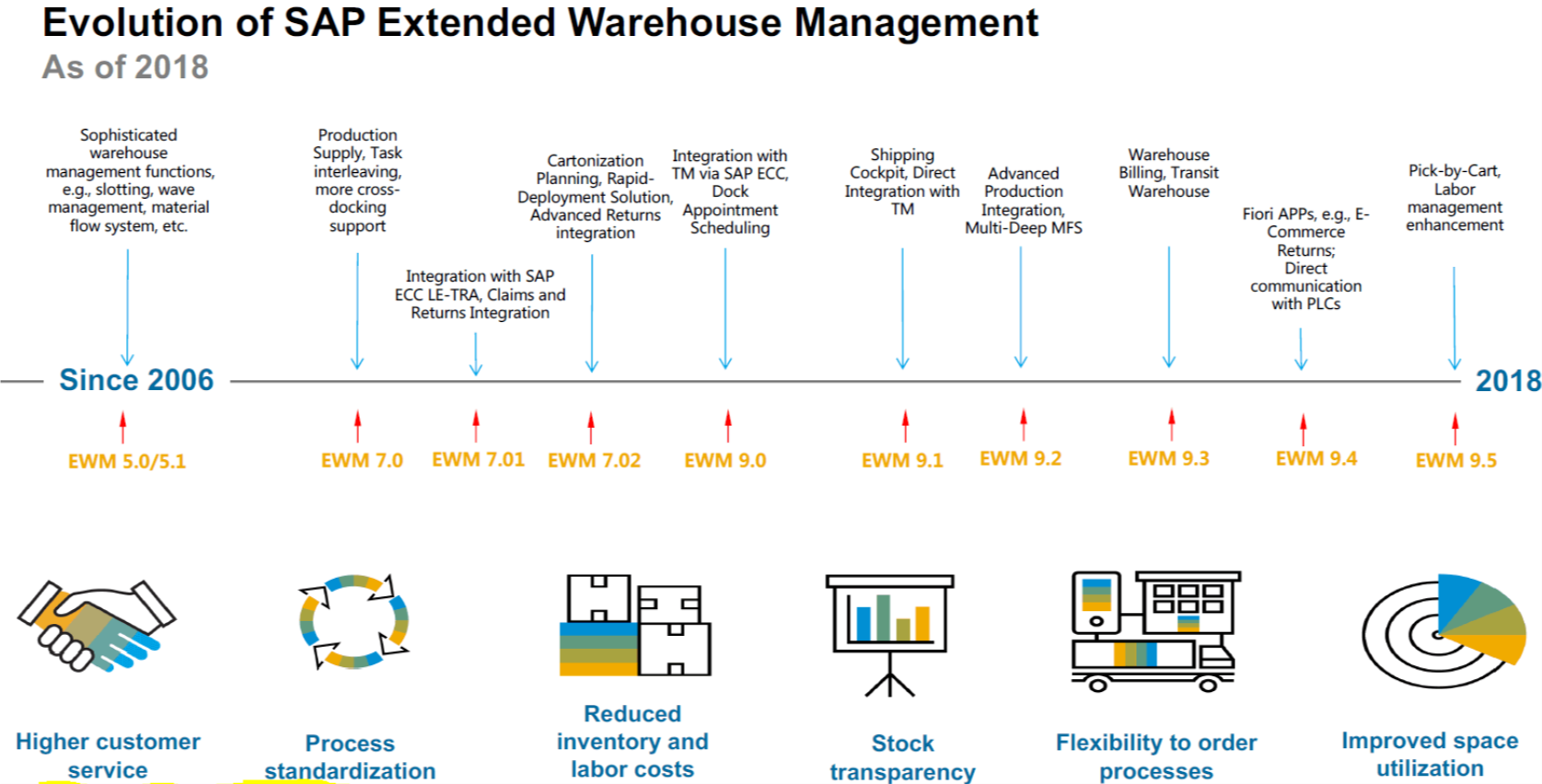
EWM has been out and in the market for quite a long time, above is the life cycle of its evolution and with addition of functionalities. Lets go thru each release or update since 2006….
- 2006 – In 2006, the last noteworthy development in the LES is made available in release ECC 6.0. SAP EWM 5.0 is already in the Ramp-Up process. With the introduction of a new system philosophy, the first release 5.0 is provided with already known and new processes and functions using a completely new system basis and document structure. The organizational units were taken over from SAP LES and supplemented by new organizational units.
- 2008 – The release SAP EWM 5.1 is another important milestone in the history of SAP warehouse logistics. With the new Material Flow System (MFS) component, the EWM now features a fully integrated material flow calculator and thus significantly stands out in comparison to the old LES.
- 2009 – In release 7.0, SAP closes the process gap in the production supply existing until then. The Cross Docking process area is supplemented by the opportunistic Cross Docking as well as the Merchandise Distribution Cross Docking.
- 2010 …….
– Dig Deeper –
S/4HANA Finance Group Reporting 1909
Q&A (Post your questions and get the answers you need)

Q. We keep hearing about “Microservices” as the cloud buzzword. Can you explain what a microservice is?
A. The concept of microservices has existed for a long time (from a service orientation architecture perspective). Recently, microservices have become popularized by enterprise software developers because it’s more lightweight and fine-grained than the SOA services.
These days custom applications deployed in the cloud are no longer built using a monolithic architecture but rather consist of smaller functionalities called microservices. SAP Cloud Platform, leveraging Cloud Foundry, supports the architecture for using microservices to build applications.
But what exactly is a Microservice?
A microservice provides a small piece of a business functionality, running its own processes and independently deployable.
The microservice architectural style is an approach to developing a single application as a suite of small services, each running in its own processes and communicating with lightweight mechanisms, often an HTTP resource API. These services are built around business capabilities and independently deployable.
Microservices usually have the following characteristics:
- Microservices are independent of each other or loosely coupled.
- Microservices can be developed in different languages.
- Microservices communicate with each other language-neutral APIs e.g., using the REST protocol.
- A microservice is individually scalable.
From an SAP cloud perceptive, Microservices are the cornerstones of Cloud Foundry, which is at the center of SAP Cloud Platform’s ability to enable Agile innovation.
You can find more details about the microservices concept at the following URL https://martinfowler.com/microservices
Cheers!