 Anthony Cecchini is the President and CTO of Information Technology Partners (ITP), an ERP technology consulting company headquartered now in Virginia, with offices in Herndon. ITP offers comprehensive planning, resource allocation, implementation, upgrade, and training assistance to companies. Anthony has over 25 years of experience in SAP business process analysis and SAP systems integration. ITP is a Silver Partner with SAP, as well as an Appian, Pegasystems, and UIPath Low-code and RPA Value Added Service Partner. You can reach him at [email protected].
Anthony Cecchini is the President and CTO of Information Technology Partners (ITP), an ERP technology consulting company headquartered now in Virginia, with offices in Herndon. ITP offers comprehensive planning, resource allocation, implementation, upgrade, and training assistance to companies. Anthony has over 25 years of experience in SAP business process analysis and SAP systems integration. ITP is a Silver Partner with SAP, as well as an Appian, Pegasystems, and UIPath Low-code and RPA Value Added Service Partner. You can reach him at [email protected].
In today’s dynamic enterprise environment, business systems like SAP, Salesforce, Workday, and Oracle underpin mission-critical processes across finance, HR, logistics, and customer engagement. As these systems evolve with continuous integration and fast-paced updates, traditional testing struggles to keep up. Manual test case creation, brittle automation scripts, and slow regression cycles all conspire to slow digital transformation.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is changing that. AI agents—intelligent software entities that perceive, reason, and act—are revolutionizing how we approach business system testing. They bring adaptability, speed, and insight to a testing process that has historically been static and reactive.
This blog explores how AI agents are transforming testing across business systems, whether or not RPA (Robotic Process Automation) is involved. We’ll demystify what AI agents actually do, how they integrate with existing tools, and how they unlock true continuous quality assurance (QA).
Testing in enterprise systems is essential but often inefficient. Consider SAP invoice processing… The test cases are manually scripted and hard to maintain. Any UI or logic changes break tests, leading to false positives. Regression testing is time-consuming and often incomplete, and this challenge multiplies across modules and integrated systems. Test teams are stretched thin, and as businesses move toward Agile and DevOps, testing becomes the bottleneck.
This is where AI and especially agents can help. But AI agents are not magical bots that test your system independently. Rather, they enhance and optimize your existing testing processes. Instead, think of them as intelligent assistants that:
- Analyze what needs to be tested
- Generate or maintain test cases
- Heal broken scripts automatically
- Prioritize high-risk test paths
- Predict failures and optimize test coverage
They don’t replace your test automation tools—they supercharge them.
Test Case Generation with AI
AI agents can scan business process models, change logs, or production usage data to auto-generate test cases. For example, if a new step is added to the invoice approval process in SAP, the AI agent identifies this and creates relevant test cases, reducing manual scripting effort.
Self-Healing Test Scripts
If a button on the Salesforce UI is renamed or a field in SAP Fiori is repositioned, traditional scripts break. AI agents use visual recognition and contextual clues to auto-update these scripts—no human intervention required
Impact-Based Test Prioritization
Rather than running an entire regression suite, AI agents analyze which parts of the system were affected by recent changes and prioritize tests accordingly. This risk-based testing reduces test cycle times dramatically.
Predictive QA and Anomaly Detection
AI agents learn from historical test results and production logs to detect anomalies, predict failure points, and recommend additional test coverage.
Conversational Test Agents
For non-technical business users or citizen developers, AI agents can act as conversational assistant.
The user can ask questions, such as:
- “Show me all failing invoice posting tests.”
- “Explain why the payroll approval flow failed.”
- “Generate tests for this new leave request workflow.”
Let’s consider how AI agents enhance regression testing in SAP without relying on RPA bots.
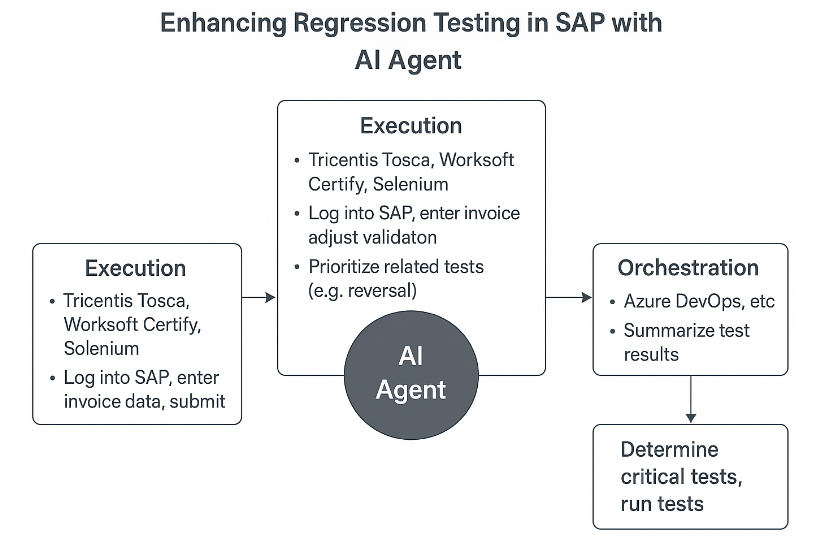
The execution of tests remains the domain of specialized automation tools like Tricentis Tosca, Worksoft Certify, or Selenium. These tools are responsible for performing interactions such as logging into SAP, entering invoice data, and submitting the form. The AI agent works alongside them, handling the analysis and maintenance tasks.
Suppose SAP has introduced a new field on the invoice entry screen, such as “Tax Code.” An AI agent trained on the existing test suite and change history would detect this layout change. It could then update the relevant test scripts to include the new field and adjust validation logic accordingly.
Beyond immediate updates, the agent might also identify related processes such as invoice reversal or approval workflows that could be affected. It prioritizes these areas for additional regression testing, ensuring comprehensive coverage without human intervention.
On the orchestration side, the AI agent integrates with a CI/CD platform like Azure DevOps. When a new build is deployed, the agent determines which tests are most critical based on recent changes. The orchestrator runs these tests, and the agent compiles a summary highlighting which workflows passed, which failed, and which require further analysis.
This collaborative model demonstrates how AI agents can reduce the test maintenance burden while improving coverage and insight.
AI agents are designed to be tool-agnostic. They work across a wide array of testing environments, seamlessly integrating with tools already in use.
In UI testing, they support frameworks such as Selenium, Cypress, and Playwright. For enterprise-grade ERP testing, they complement tools like Tricentis Tosca and Worksoft. When dealing with APIs, they enhance testing in platforms like Postman and SoapUI. For test management, they interface with Jira/Xray and TestRail, and they hook into Jenkins, GitLab, or Azure DevOps for orchestration.
The point is not how the tests are executed, but how intelligently they are created, prioritized, maintained, and analyzed.
The benefits of incorporating AI agents into business system testing are significant. They enable faster test creation and execution, allowing teams to keep pace with frequent updates. By automatically adjusting scripts when interfaces change, they reduce the maintenance load that typically slows down test cycles.
AI agents also provide broader coverage by uncovering edge cases and generating diverse test paths from real usage data. Their ability to analyze and predict failure points means that testing becomes smarter and more targeted over time.
This adaptability is especially valuable in integrated environments where a change in one module can have cascading effects. AI agents ensure that these relationships are understood and tested appropriately.
Transforming your QA strategy begins with an honest assessment of your current maturity. Where are the bottlenecks? Are scripts breaking too often? Are regression cycles too long? Understanding these gaps helps focus your AI strategy.
Next, select an AI agent framework that fits your technology stack. Scriptless tools like Testim or Mabl come with built-in AI capabilities. For teams using Selenium, add-ons like Test.AI or Functionize can introduce AI without major disruption. Custom agents can also be developed using LLM platforms like OpenAI, Gemini, or Azure OpenAI, tailored to specific workflows.
Once a framework is in place, feed it relevant context—test execution logs, business process documentation, production usage patterns, and recent change histories. This data helps the agent learn how your systems work and what needs to be tested.
Start with a targeted pilot. Choose high-impact scenarios such as invoice processing, payroll runs, or customer onboarding workflows that frequently change or historically break. Measure outcomes: Was test maintenance reduced? Were new defects detected? Was cycle time improved?
As confidence builds, scale your AI-driven testing across modules and business units. Integrate AI agents into your CI/CD pipeline and ensure test governance policies account for AI-generated recommendations.
Navigating Common Challenges
Introducing AI agents into QA does come with challenges. Data privacy must be protected, particularly when training AI with production logs. Masking sensitive information or using synthetic data can address this risk.
Resistance to change is another factor. QA teams may fear that AI will replace their roles. Clear communication that AI is a co-pilot—not a replacement—can help, as can training on how to use and interpret AI outputs.
Tool proliferation is also a concern. Instead of adopting entirely new stacks, prioritize solutions that integrate with what you already use.
Finally, transparency is critical. Some AI-driven tools operate as black boxes. Favor platforms that offer explainability—clearly showing why certain tests were prioritized or why a script was altered.
Looking ahead, AI agents will evolve from test enhancers to autonomous QA orchestrators. They will not just respond to change, but anticipate it. Test suites will update themselves as business logic evolves. AI agents will collaborate with CI/CD systems to run targeted regressions on demand. Dashboards will highlight not just test results, but risk exposure and release readiness, backed by predictive models.
System drift—subtle deviations in process behavior over time—will be detected before it causes failures. Quality assurance will no longer be a phase, but a continuous, intelligent service woven into every aspect of enterprise development and operations.
Summary
AI agents are redefining the future of business system testing. Far from being limited to RPA workflows, they deliver value across all enterprise applications by making testing more intelligent, adaptive, and proactive.
They do not replace testers. They empower them, turning manual effort into strategic oversight. With AI agents handling routine analysis, maintenance, and prioritization, QA professionals can focus on improving test strategy, aligning with business objectives, and ensuring system resilience.
In a world where agility is paramount, and failure is costly, AI-powered testing is not just beneficial—it is essential. Now is the time to evolve your approach and embrace AI agents as vital partners in your testing journey.




