Shailesh Mishra is a SAP EWM Senior Consultant. Shailesh has deep Expertise in implementing and offering SAP EWM best practices solution and EWM deployment options on S/4 Hana embedded versions and decentral versions supporting various business verticals like Pharma, Food industry and Manufacturing. Cross module knowledge of SAP ERP logistics like SAP MM, SD and Production Planning. Strong technical knowledge of SAP ABAP. You can reach him at [email protected].
Shailesh Mishra is a SAP EWM Senior Consultant. Shailesh has deep Expertise in implementing and offering SAP EWM best practices solution and EWM deployment options on S/4 Hana embedded versions and decentral versions supporting various business verticals like Pharma, Food industry and Manufacturing. Cross module knowledge of SAP ERP logistics like SAP MM, SD and Production Planning. Strong technical knowledge of SAP ABAP. You can reach him at [email protected].
This month we wanted to introduce you to a new blogger for IT Partners. His name is Shailesh Mishra and is a very Senior EWM SAP consultant. I am sure you will enjoy this, his first, and many more articles to come…..
Before we tackle the origin and eventual evolution of EWM SAP, lets get a quick understanding of what it is….

If you currently manage your warehouse stocks using the application component Inventory Management (MM-IM), then you manage material stock based on quantity and value in several storage locations.
In contrast, EWM gives you the option of mapping your entire warehouse complex in detail in the system, down to storage bin level. Not only do you gain an overview of the entire quantity of a material in the warehouse, you can also always determine exactly where a certain material currently is in your warehouse complex. With EWM, you can optimize the use of various storage bins and stock movements and can store together material stocks from several plants in random storage areas. Using EWM, you can control and optimize processes in the warehouse.
Extended Warehouse Management is completely integrated into Inventory Management and Delivery Processing. Business processes, which you trigger in other application components, lead to physical goods movements in your warehouse. You organize, control, and monitor these goods movements using EWM.
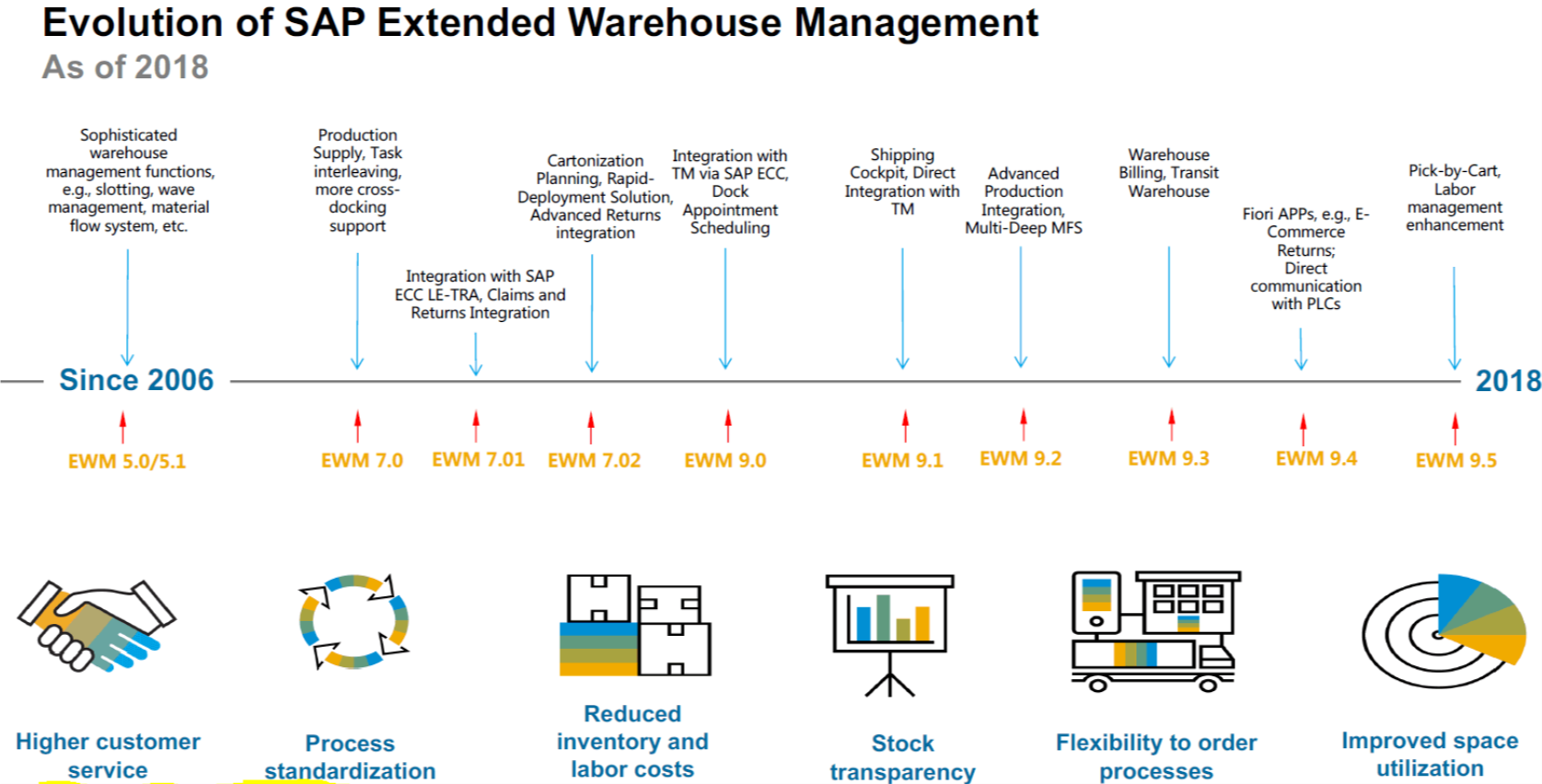
EWM has been out and in the market for quite a long time, above is the life cycle of its evolution and with addition of functionalities. Lets go thru each release or update since 2006….
2006 – In 2006, the last noteworthy development in the LES is made available in release ECC 6.0. SAP EWM 5.0 is already in the Ramp-Up process. With the introduction of a new system philosophy, the first release 5.0 is provided with already known and new processes and functions using a completely new system basis and document structure. The organizational units were taken over from SAP LES and supplemented by new organizational units.
2008 – The release SAP EWM 5.1 is another important milestone in the history of SAP warehouse logistics. With the new Material Flow System (MFS) component, the EWM now features a fully integrated material flow calculator and thus significantly stands out in comparison to the old LES.
2009 – In release 7.0, SAP closes the process gap in the production supply existing until then. The Cross Docking process area is supplemented by the opportunistic Cross Docking as well as the Merchandise Distribution Cross Docking.
2010 – The release 7.01 includes expansions regarding the Material Flow System (MFS). On the performance side, the response times of the telegram exchange have been improved. The functions now also cover the requirements related to controlling the container conveyor equipment.
2011 – The release 7.02 reflects the replacement of the old SAP LES. Using migration tools for taking over the master data and processes from the SAP LES as well the Rapid Deployment Solution (RDS), a fast deployment of and conversion to SAP EWM shall be made possible.
2013 – With the release 9.0, SAP combines its three systems Extended Warehouse Management (EWM), Transportation Management (TM) and Event Management (EM), that are most important for the operative logistics, on the common system platform SAP Supply Chain Execution (SCE), thereby offering a lot of potential for optimizing the entire supply chain. Apart from the integration with TM and EM, EWM 9.0 offers a number of new functions. As far as the problem of changing quantities in delivered packaging is concerned, the standard version of EWM 9.0 offers a solution by using stock-specific units of quantity that will significantly facilitate the goods issue processes with different packaging units.
2014 – The released 9.1, on May 2014.
2015 – The released 9.2, on April 2015.
2015 – The released 9.3, on November 2015.
2016 – The released 9.4, on May 2016.
2017 – The released 9.5, on November 2017. SAP includes foremost additional functions in labor management, improvements in retail and e-commerce and the integration of SAP Global Batch Traceability (GBT)
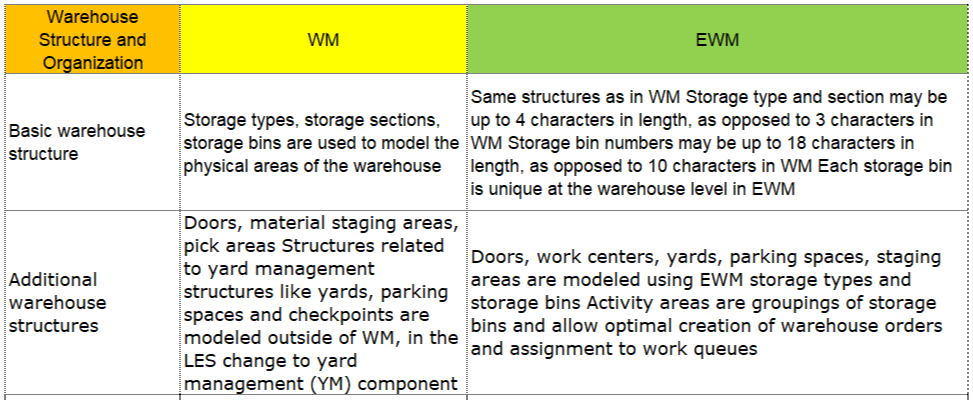
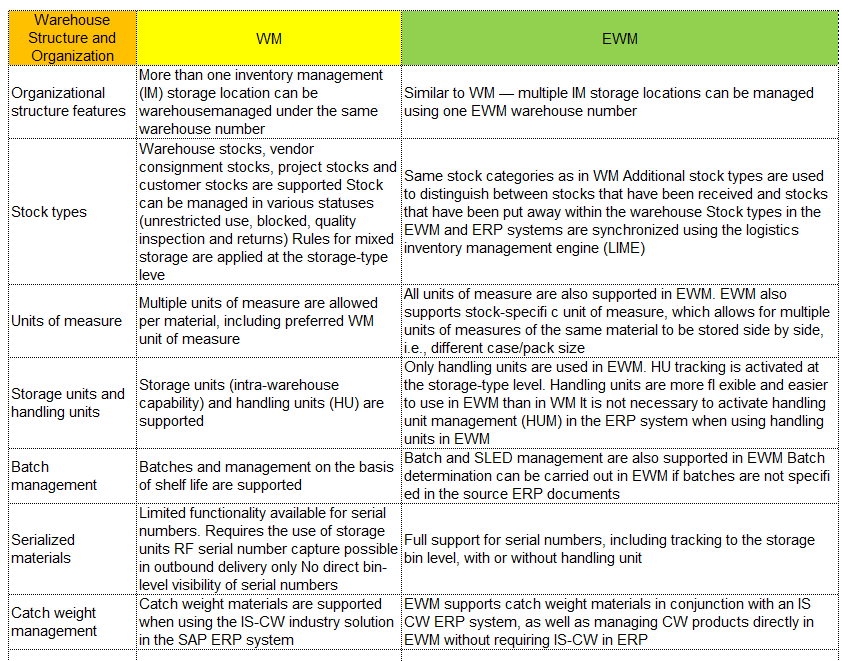
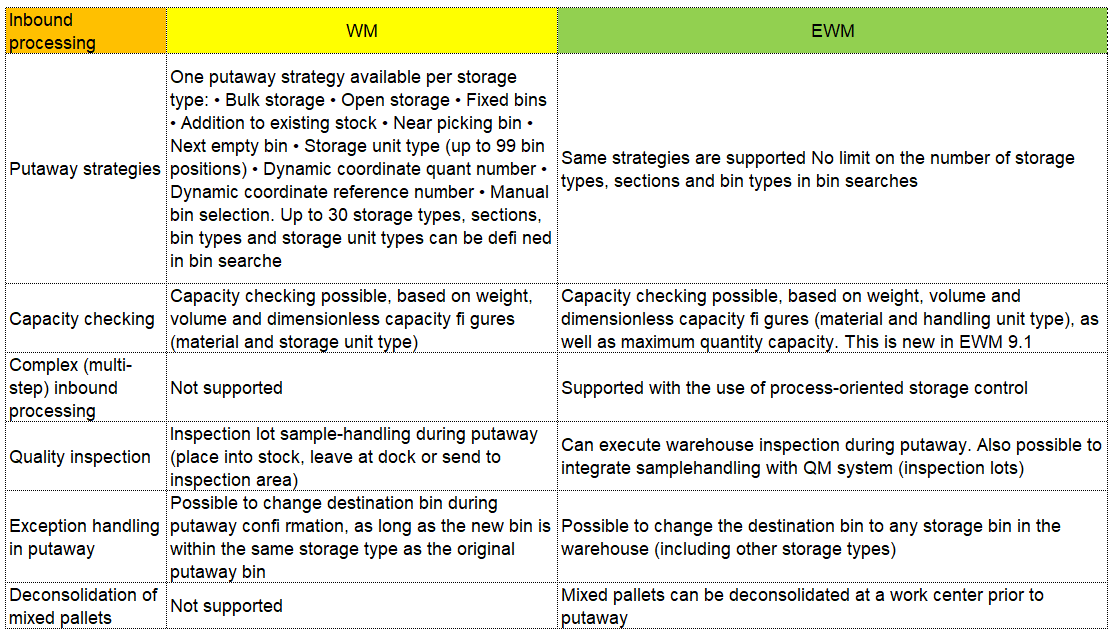
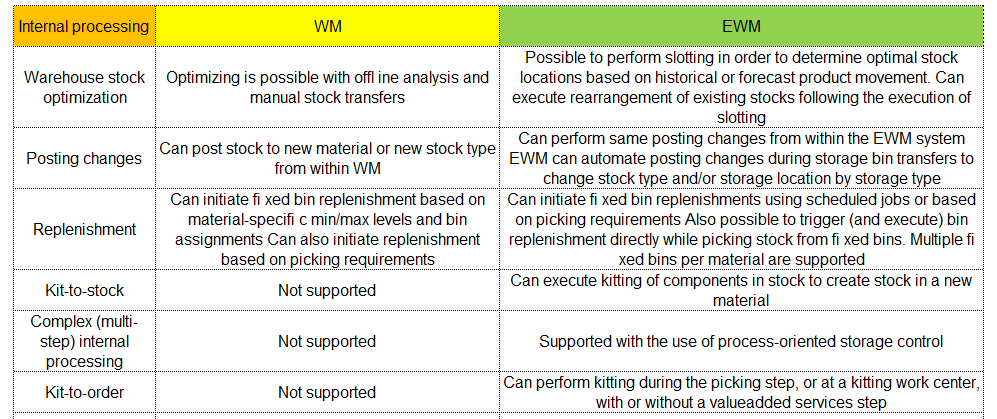
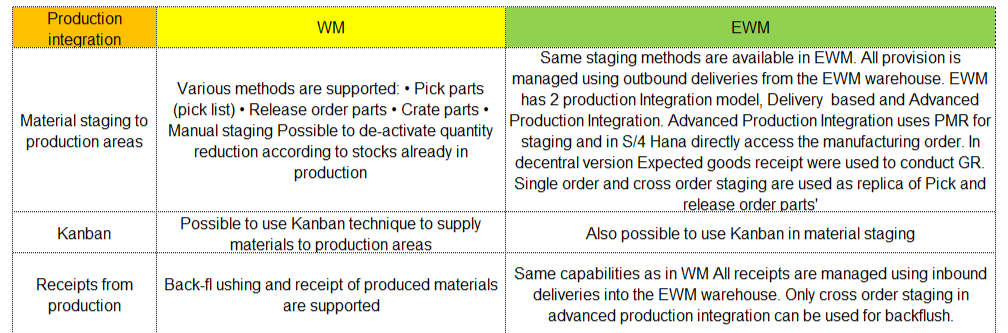
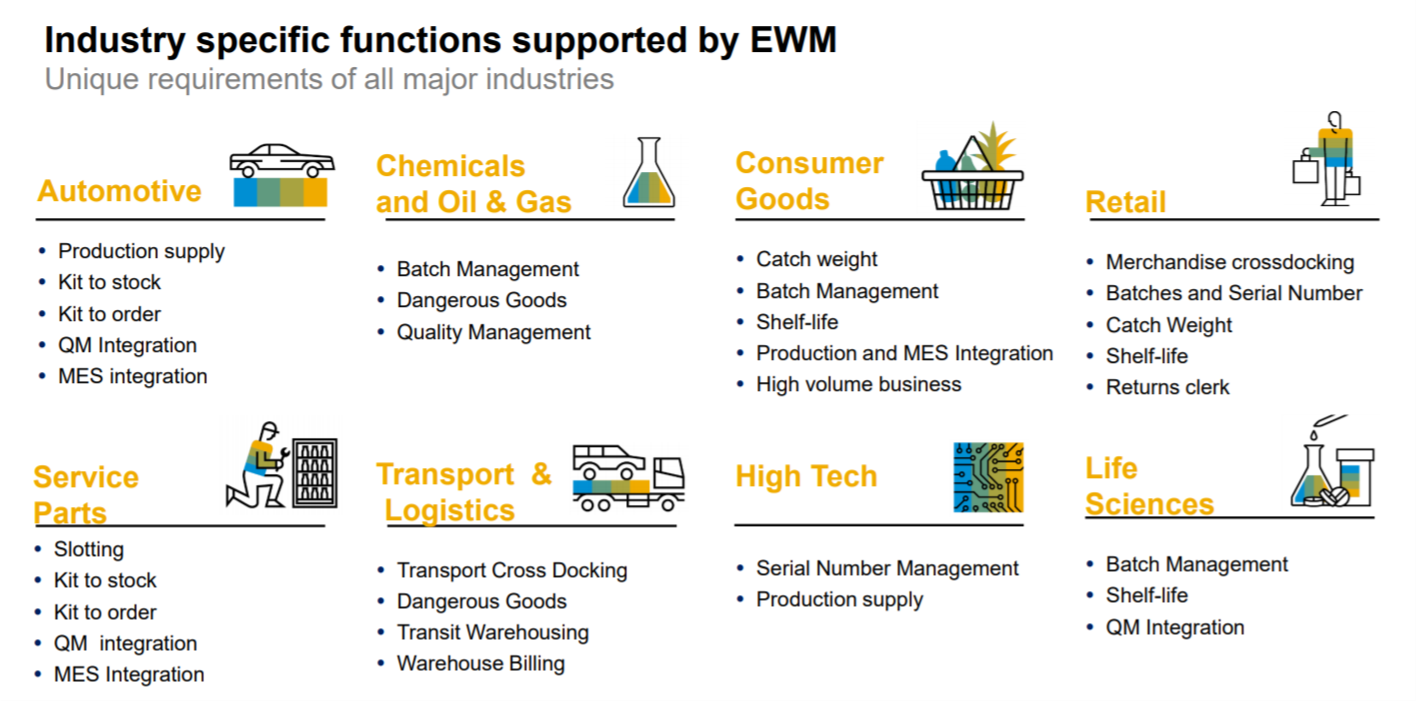
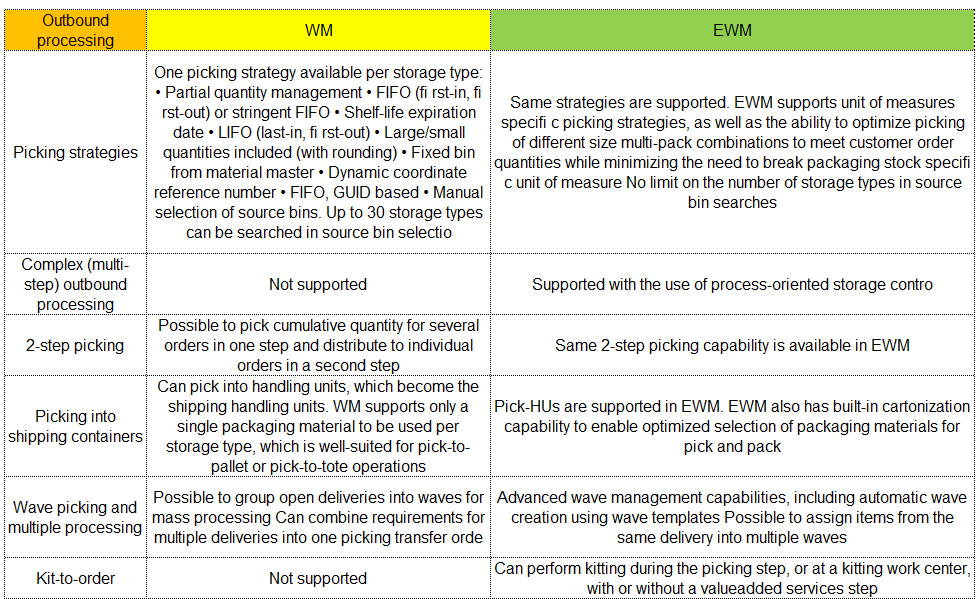
I can hear some of you saying, wait I thought SAP’s Warehouse Management Solution was called WM for Warehouse Management? Well you are right, but wait there’s more… SAP WM(Warehouse Management) and SAP EWM(Extended Warehouse Management) are both modules of SAP. They have a lot of similarities but SAP EWM has additional features for key activities in the Warehouse.
For instance, SAP EWM is more flexible in designing the warehouses and processes compared to SAP WM. SAP EWM has additional features compared to SAP WM like an RF framework, Warehouse structure, picking, posting and managing storage bins as examples.
Summary
With SAP’s Extended Warehouse Management (EWM) on-premise or cloud deployment, you can manage high-volume warehouse operations and integrate complex supply chain logistics with your warehouse and distribution processes – delivering the ultimate in visibility and control. Optimize inventory tracking, cross-docking, distribution operations, multichannel fulfilment, and more – all in real time.