Anthony Cecchini is the President and CTO of Information Technology Partners (ITP), an ERP technology consulting company headquartered now in Virginia, with offices in Vienna and Herndon. ITP offers comprehensive planning, resource allocation, implementation, upgrade, and training assistance to companies. Anthony has over 20 years of experience in SAP business process analysis and SAP systems integration. ITP is an Appian, Pegasystems, and UIPath Low-code and RPA Value Added Service Partner. You can reach him at [email protected].
Anthony Cecchini is the President and CTO of Information Technology Partners (ITP), an ERP technology consulting company headquartered now in Virginia, with offices in Vienna and Herndon. ITP offers comprehensive planning, resource allocation, implementation, upgrade, and training assistance to companies. Anthony has over 20 years of experience in SAP business process analysis and SAP systems integration. ITP is an Appian, Pegasystems, and UIPath Low-code and RPA Value Added Service Partner. You can reach him at [email protected].
Last month we discussed the latest release of S/4 Hana, release 1909. This month I would like to take a look at BW4HANA. SAP BW/4HANA is a new data warehousing application with significant improvements from SAP Business Warehouse (BW) on HANA. Released in 1998, the original BW gave customers the ability to offload data reporting features to improve performance time. There were no SAP updates until 2012 when it first released SAP BW powered by SAP HANA. In 2016, the release of BW/4HANA included some functionalities from the original SAP BW, but also added several new features and newly designed interface.
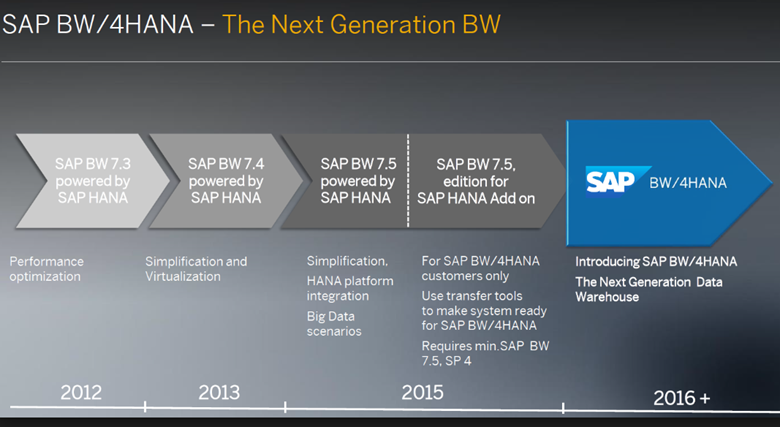
BW/4HANA intends to provide real-time insight on data, across a diverse IT landscape to allow a single harmonized view on the data (“single point of truth”). It tends to minimize the movement of data across the data warehouse layers and simplifies the connectivity with external data sources. A redesigned version of the classic Layered Scalable Architecture best practices (under the concept of LSA++) offers a new framework to convert the data warehouse into the BW HANA-Optimized version. BW/4HANA also leverages in-memory capabilities of the HANA database, offering with this platform a performant analytics solution, which can handle huge volumes of data (e.g. IoT, Big Data).
SAP BW/4HANA Platform can be deployed On-Premise and in the Cloud and can consume SAP and non-SAP data sources.
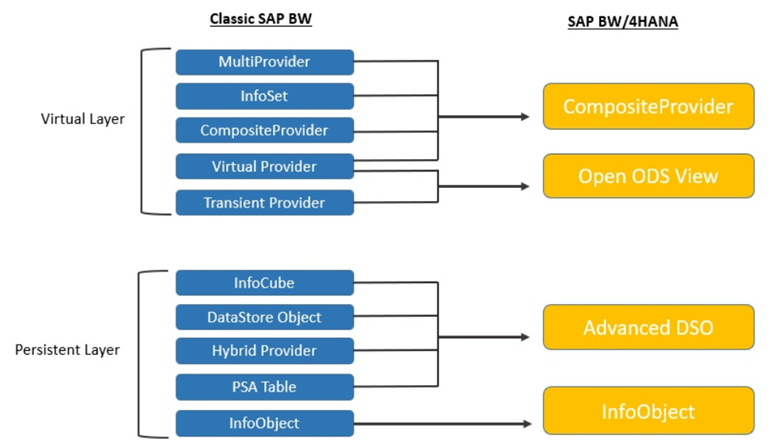
SAP BW/4HANA limits the number of object types for data modeling. The Simplified Object Model eliminated InfoCubes and other legacy objects. Some legacy objects, like InfoObjects, are now optional. SAP BW/4HANA restricts objects to Open ODS views, CompositeProviders, and Advanced DSOs (and optional InfoObjects) to simplify the application development process.
Lets define these….
- Composite Provider: this object combines data from other InfoProviders (join/union) and makes the data available for reporting
- Open Operational Data Store View: this object acts as an interface between the SAP HANA objects (e.g. SAP HANA tables, views) and the BW modeling part for further modelling. It makes it possible to consume external data sources in BW without staging, combine data sources with BW models and physically load data from external data sources. They allow integration without having to create BW InfoObjects (field-based modeling)
- Advanced DSO: they are required to persistently store the data. It replaces the traditional Data Store Object, Persistent Staging Area (PSA) or InfoCube
- InfoObjects: like the classic BW version, they are mainly used to build data models and can be defined as key figures or characteristics
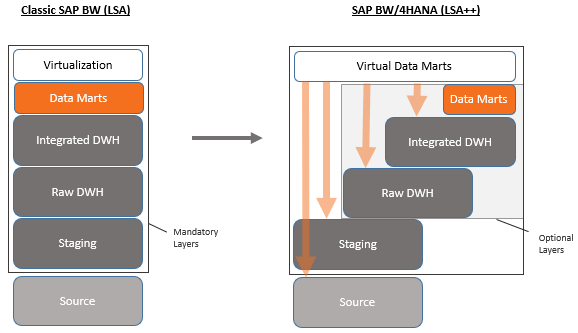
Traditional data warehouses are built upon the Layered Scalable Architecture best practices (LSA). It is based on several layers with data being physically transferred (e.g. Acquisition, Transformation, Data Marts Layer). The new LSA++ architecture offers a much simpler and smaller landscape which relies more on virtual objects and avoids duplicating data between layers without compromising the performance.
SAP BW/4HANA is a new product with a new code base, which is not part of SAP NetWeaver, meaning it is decoupled from the SAP NetWeaver Release Cycle and not all components are part of BW4/HANA. However, certain NetWeaver components are still part of the BW/4HANA shipment. For example, Application Lifecycle Management, such as patching, and Service Packs and Transports of BW models through the environment landscape, will still be handled in the same way as currently the NetWeaver infrastructure.
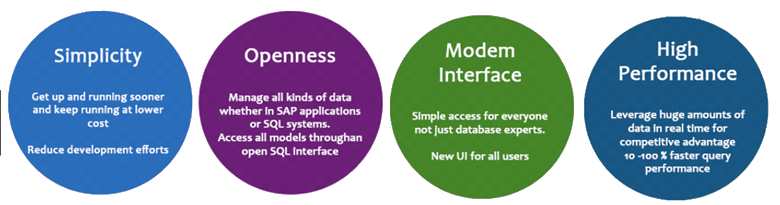
That be said, SAP did develop SAP BW/4HANA with emphasis that it be built on the following 4 design principles: Simplicity, Openness, High Performance and Modern Interface. lets look at each in turn…
SAP BW/4HANA Design Principle: Openness
SAP designed BW/4HANA with work with multiple sources of data including Hadoop or Cloud, whether structured and unstructured. This flexibility allows BW/4HANAto consume data in a variety of data types and formats. SAP BW/4HANA is open to integrating data from social media, third-party databases, and social media. It does this through a four-component approach: operational data provisioning (ODP), SAP HANA source system, big data source system, and a file source system.
SAP BW/4HANA Design Principle: Simplicity
SAP BW/4HANA aims to reduce the complexity of the development environment and decrease the end-to-end development time. BW/4HANA has reduced the number of modelling objects from 10 to 4. Two of the objects will allow for persistency of data and 2 objects are for virtualization that allows for fewer layers. SAP BW/4HANA reduces the number of steps needed to perform maintenance and business processes. Enterprise data warehousing is simplified in BW/4HANA by limiting the types of data objects. InfoObjects stay the same while DSOs serve the same functions as InfoCubes, Hybrid Providers, and PSA’s did in SAP BW. Similarly, Composite Provider objects replace InfoSets and MultiProviders Virtual cubes are now open ODS views.
This simplification helps to make the architecture leaner and more flexible, and less development effort. The reduction in persistence of data cuts down the data foot print. Along with SAP’s increased capability for Cloud deployment, including HANA Enterprise Cloud, Microsoft Azure and Amazon Web Services, this all leads to helping bring down the TCO for BW/4HANA..
SAP BW/4HANA Design Principle: Modern Interface
To align to the changes in the BW/4HANA, simpler and more modern interfaces are available for business users, developers and administrators. For Business users, the BEx interface is no longer available (although BEx Queries still form part of the solution), and BW/4HANA has tighter integration with the SAP Business Objects BI toolset, as well as SAP Business Objects Cloud. The developer interface is via the Modelling tools integrated into SAP HANA Studio and Eclipse, and from an administrator perspective, UI5 tools such as the UI5-based Process Chain Monitor are available as a replacement for the ABAP Process Chain Monitor.
SAP BW/4HANA has replaced most of the SAP GUI screens with a new Eclipse-based UI and intends to replace all the SAP GUI. The Data Flow Modeler is more than a visualization tool. The interactive data model allows you to drag and drop, drill down to configurations, and visually interact with the data flow
SAP BW/4HANA Design Principle: High Performance
BW/4HANA is designed to push an increased amount of OLAP functionality and computation to the HANA database as well as for the Planning and Data Management elements. But the higher performance for BW/4HANA is not just about pushing the workload to the HANA engine. It is also about the greater integration to leverage the HANA platform capabilities within BW, for example, integrating data from a HANA model into a BW model. In addition, BW/4HANA provides the capability to leverage various advanced analytical libraries and algorithms for data mining or predictive analytic scenarios.
BW/4HANA Data Life cycle Management
BW/4HANA simplifies data management with a multi-temperature strategy. SAP BW/4HANA uses intelligent data classifications for storing data according to accessibility requirements. Cold/frozen data that needs to be saved for legal or regulatory requirements can be moved to SAP IQ or Hadoop. BW/4HANA stores warm data that is rarely needed in FlashArray which is controlled by HANA. Hot data is stored in the SAP Hana in-memory database for immediate access and processing.
Preconfigured Industry Specific Data Models
SAP is creating preconfigured data models for specific industries and business operations using LSA++ and BW/4HANA objects. This content allows customers to simplify data flow and analytics.
Summary
SAP envisions BW/4HANA as an unrestricted data warehouse solution for the modern enterprise-level organization. Data warehousing is a consolidation of corporate and extra-corporate data than can be analyzed for decision-making and innovative new products. Look for future releases to integrate more tightly with Hadoop and provide big data lakes, machine learning, and intelligent data analysis.