Shailesh Mishra is a SAP EWM Senior Consultant. Shailesh has deep Expertise in implementing and offering SAP EWM best practices solution and EWM deployment options on S/4 Hana embedded versions and decentral versions supporting various business verticals like Pharma, Food industry and Manufacturing. Cross module knowledge of SAP ERP logistics like SAP MM, SD and Production Planning. Strong technical knowledge of SAP ABAP. You can reach him at [email protected].
Shailesh Mishra is a SAP EWM Senior Consultant. Shailesh has deep Expertise in implementing and offering SAP EWM best practices solution and EWM deployment options on S/4 Hana embedded versions and decentral versions supporting various business verticals like Pharma, Food industry and Manufacturing. Cross module knowledge of SAP ERP logistics like SAP MM, SD and Production Planning. Strong technical knowledge of SAP ABAP. You can reach him at [email protected].
Back this month and kicking off the new year is Shailesh Mishra with another great Extended Warehouse Management (EWM) blog on the Outbound Process with Pick, Pack, Stage and Load in S/4 HANA Embedded 2020.
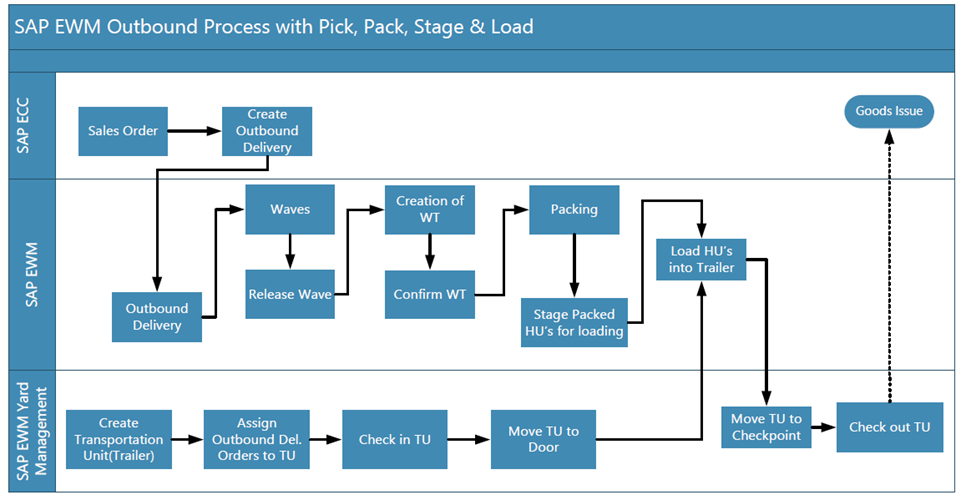
This business process is primarily used when Warehouse send the bigger quantities (For example, Cartons or pallets) to the customers. The goods are picked by ”Waves” into pick handling units (Pick HUs) and consolidate them into shipping HUs at a packing station. The goods are further packed into shipping HUs and load them into a truck before posting goods issue.
The pick HUs are generally a wire basket or Cart, or forklift which can be an equipment to carry out the process of picking.
Alternatively, customer can also use process of Pick HU as ship HU where pallets are directly picked and brought to staging area. In this process, packing step is skipped.
This blog is written to explain how SAP EWM outbound Storage control using POSC can be leveraged for outbound process undergoing Pick, Pack, Stage and Load Process.
Process Scenario
The following graphic shows the overall process of the EWM SAP Outbound Pick,Pack,Stage and Load
Before, we jump into process, it is imperative to understand SAP EWM Wave Management.
Grouping of warehouse request items to control warehouse activities, for example, picking, or posting changes.
These groupings are then processed together in subsequent processes, for example, the transfer of all warehouse request items assigned to a wave at a certain point in time to warehouse task creation. The warehouse tasks created are then forwarded to warehouse order creation
EWM SAP combines warehouse request items and split items into waves based on criteria such as activity area, route, or product.
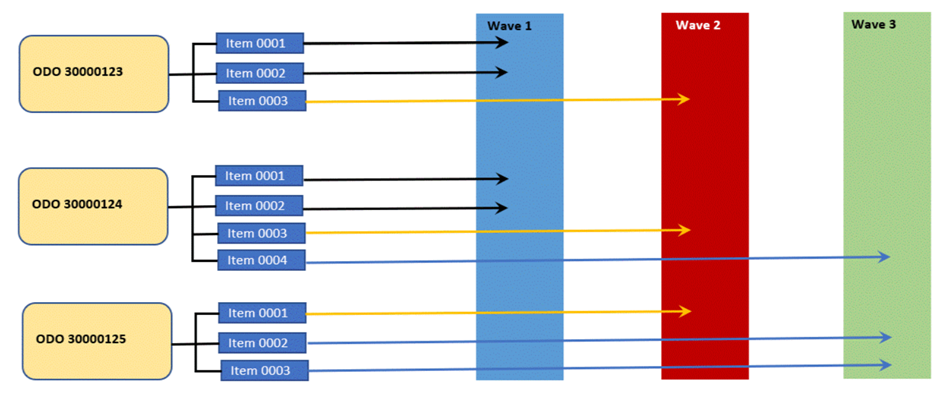
The warehouse request items can be clubbed into waves as below based on certain criteria like route, ship to party, carrier. SAP EWM uses condition technique to consolidate the warehouse request into Waves.
Waves are further released manually or automatically. For better, warehouse operation SAP recommends releasing waves automatically.
Replication Steps in a hana 2020 system
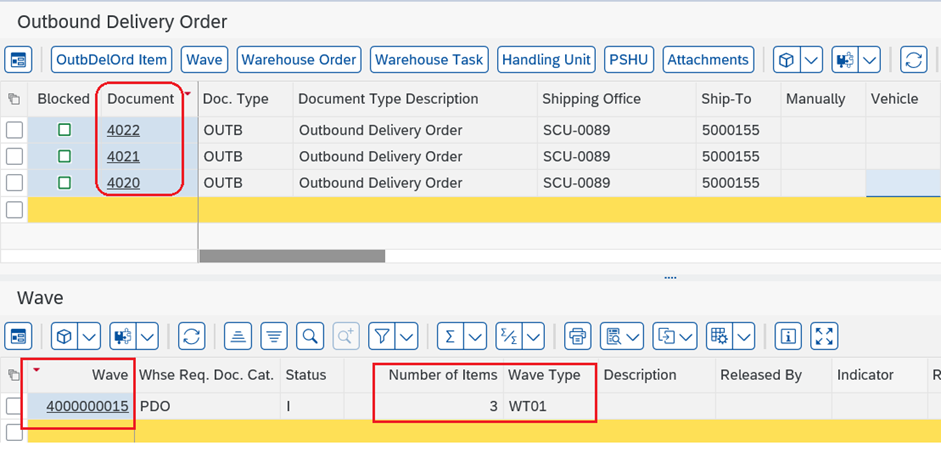
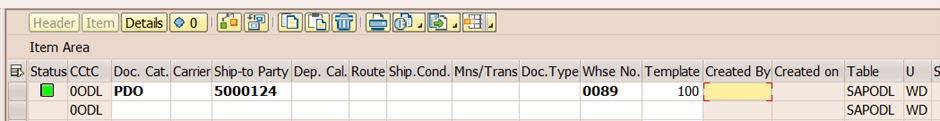
Step 1: Check the warehouse request items in Warehouse Monitor App in EWM. 3 warehouse requests are created. /SCWM/MON or in Fiori App.
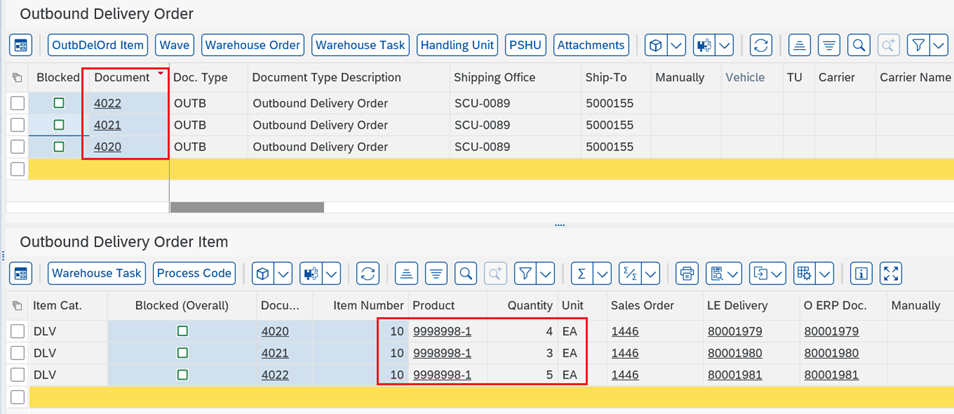
Step 2: Waves are created in EWM. Check in Monitor.
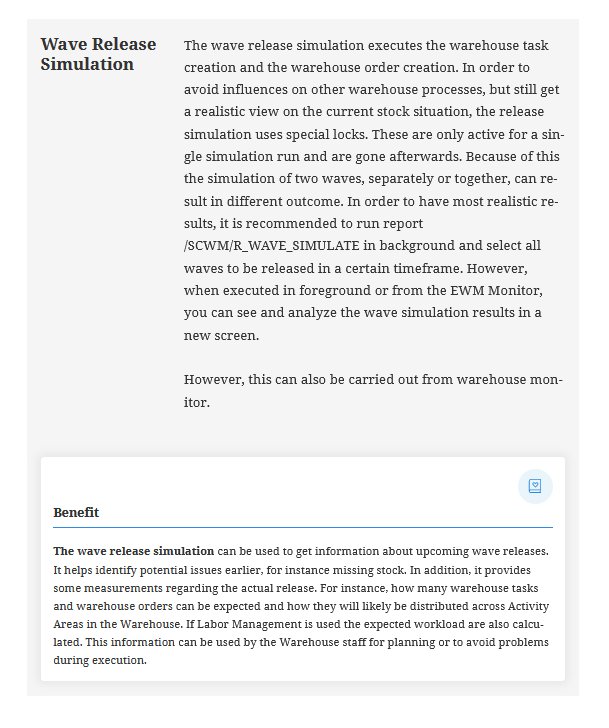
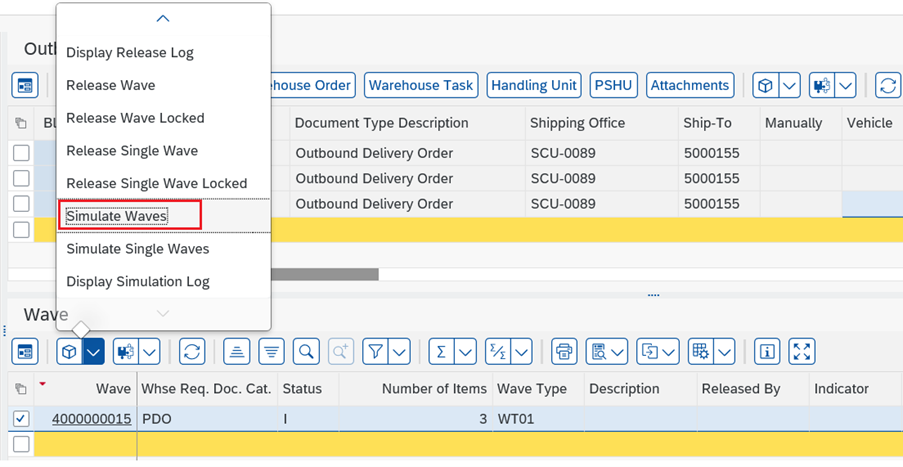
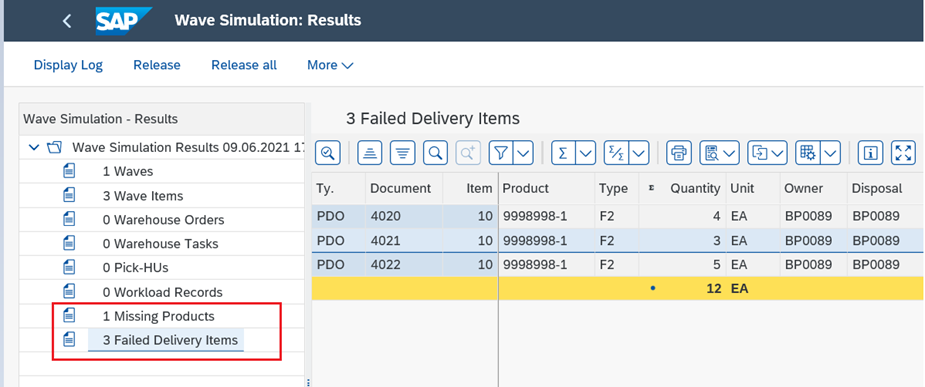
The next process is to release the Waves. From S/4 HANA 1909 FPS01, SAP has introduced a new feature called as ”Wave Release Simulation”. This simulation tool when performed from warehouse monitor gives an early indication of missing parts in stock which helps in analyzing the frequently failed warehouse task creation from outbound delivery orders in EWM.
System triggers an error that 1 product is missing, so warehouse operator needs to find the root
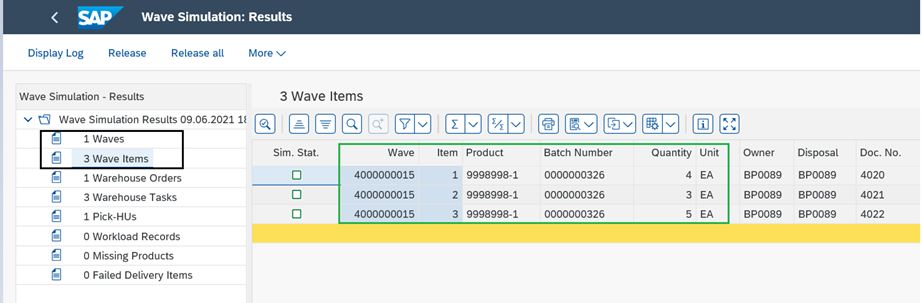
Wave is passed wave release simulation, now trigger actual wave release. System created the required WTs for further picking process.
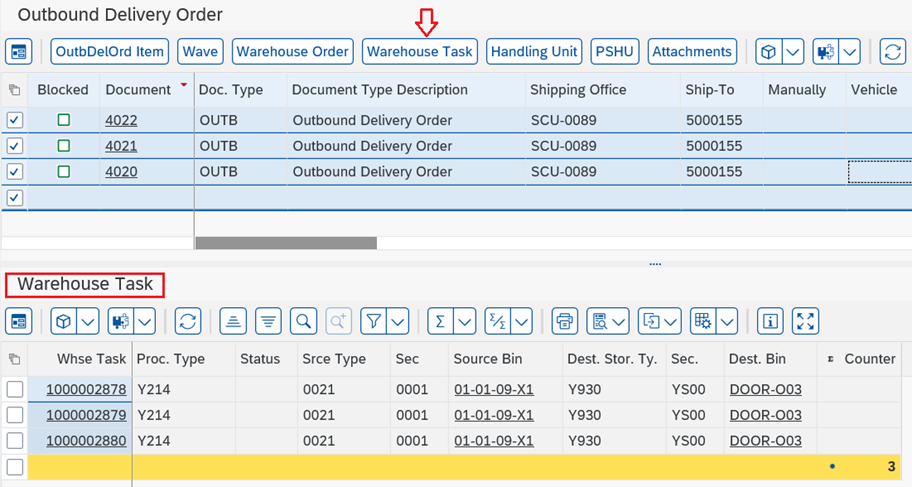
Upon the wave release (Automatically or manually), the system creates warehouse tasks (WTs). The system joins the WTs together into warehouse orders (WOs) to optimize the working packages for the pickers. The WOs are used to pick the goods and move them to a packing station. The WOs are assigned to different queues according to specific criteria such as the activity area and the type of resource necessary to access the storage bins. Within one WO, the WTs are sorted according to specific criteria such as the pick path.
.
WTs are sorted by Pick Path and then bundled so that the shortest path is covered when pickers are working in different activity area. However, with this sorting method, products must be brought to a packing work center to consolidate deliveries.
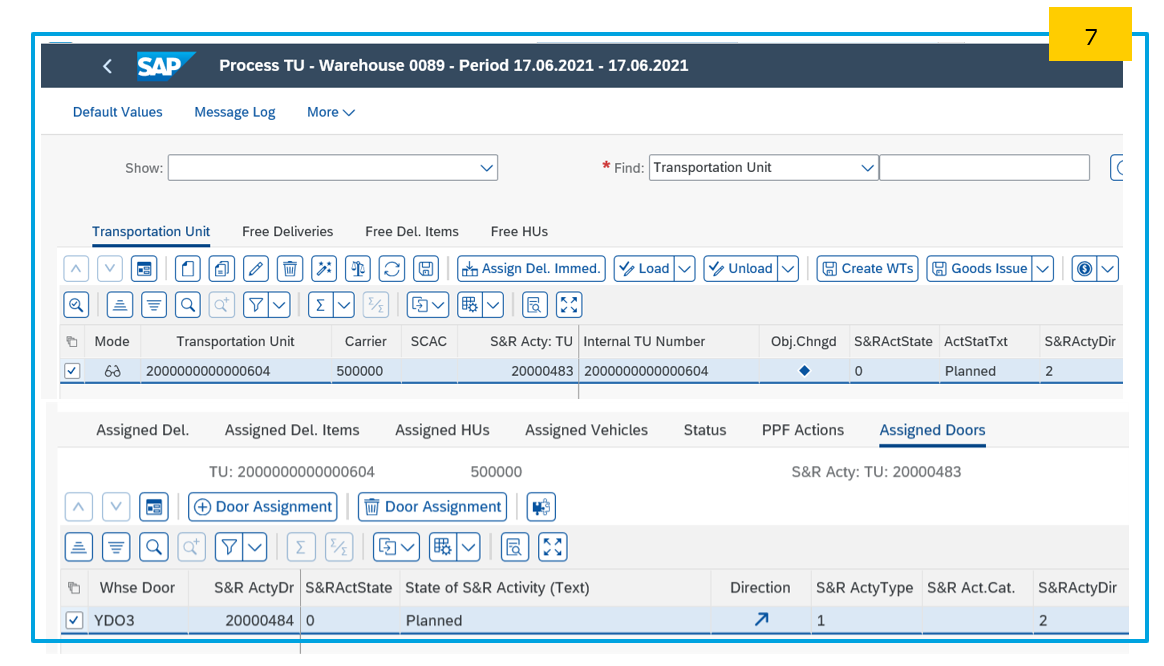
Step 3: Create Transportation Unit (TU) in EWM and assign it to door as per ODO. For, this TU creation, we are taking a separate and new Warehouse task, other than above.
TU is created and assigned to door
Step 4: Pick the goods through radio frequency device using /SCWM/RFUI, carry out the picking activity.
During picking, warehouse worker picks the goods and brings them to the packing station. This step is carried out using an RF device.
The warehouse worker goes to the starting point for picking, chooses the equipment necessary for the picking (for example, a vehicle and an RF device) and logs on as a resource. The warehouse worker puts a wire basket as the pick-HU (not created in the system yet) onto the vehicle. Each pick-HU has a permanent HU number and bar code on it.
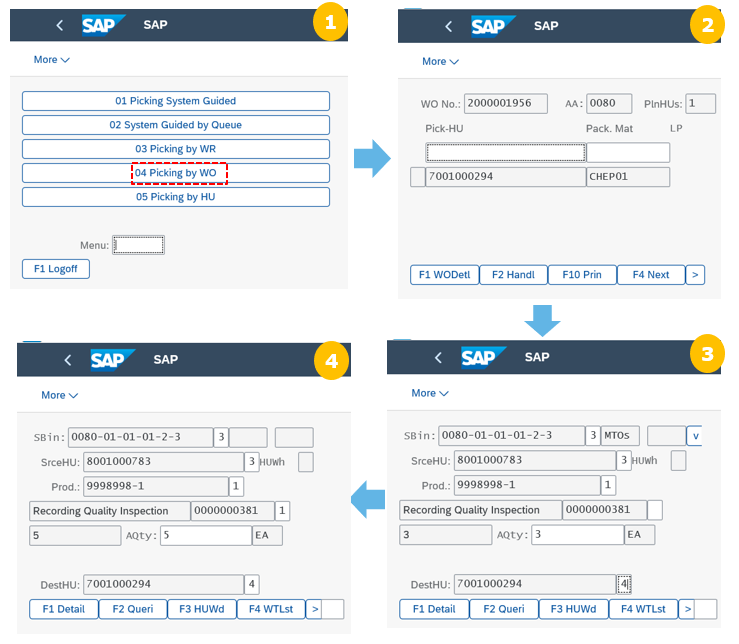
The warehouse worker scans the WO. System prompts to create the pick-HU for this WO. For this purpose, user scans the bar code of the pick-HU.
User then drives to the first source bin of the first WT displayed on the RF device, picks the required quantity of the product, and puts the product into the pick-HU proposed by the system. To verify that the WT is carried out correctly, user scans data such as source bin, product, pick-HU to verify the data and enters the quantity. After all fields have been verified, the WT is confirmed, and the worker proceeds with the execution of the next WT displayed on his or her RF device.
After the last WT of the WO is confirmed, the warehouse worker is prompted to bring the pick-HU to the packing station. User moves the pick-HU from the resource to the packing station and confirms this step in the system.
User then returns to the starting point for picking to prepare the pick-HU for the next WO.
The Pick HU is created, and Pick WO is confirmed. The Pick HUs are now moved to packing work center
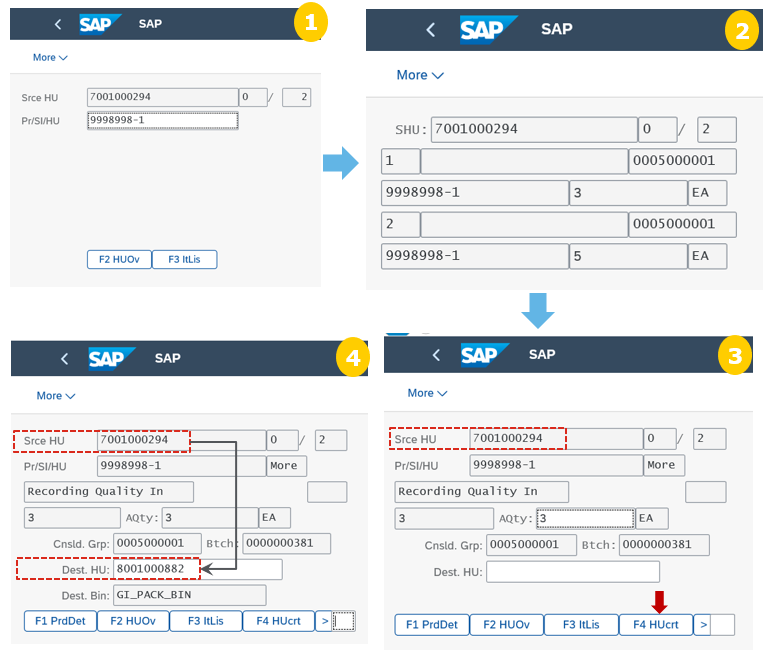
Step 5: Repack the products into shipping HU at packing work center.
At the packing station, a warehouse worker packs the goods into shipping HUs for each consolidation group. A consolidation group is used to group the goods that should be packed and shipped together (for example, for one specific customer and route). The packer can use the monitor to know when to start packing for a certain consolidation group and what kind of packaging material to be used (see the monitoring section below).
The packer takes a packaging material and creates a HU. User prints a HU identification label and moves the goods from a pick-HU to the shipping HU. User scans the pick-HU, the product to be repacked, and the shipping HU. The system creates internally a WT for the movement of the product from the pick-HU to the shipping HU and confirms it immediately. The empty pick-HU is deleted automatically upon the WT confirmation. The wire baskets are returned later to the starting point.
Once a shipping HU has been completely packed (the HU is physically full or there are no more open WTs for the consolidation group), it is weighed, and an additional label is printed. It contains HU information such as the customer, route, weight, and volume. The packer confirms the completion of the shipping HU in the system. This triggers the creation of an HU WT to move the HU to the staging area.
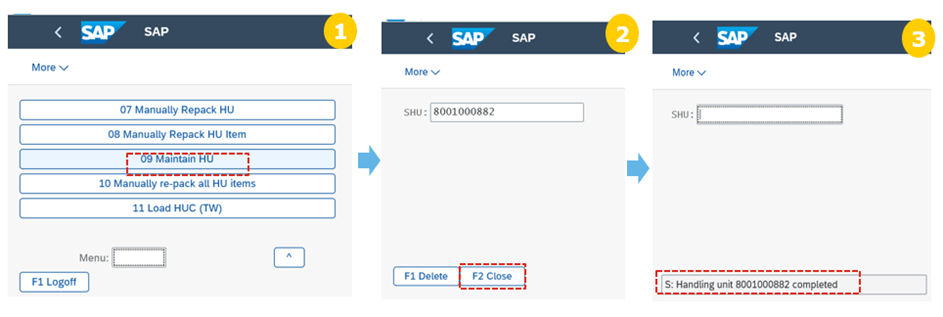
Step 6: Close the shipping HUs, the shipping HUs are closed (the Packing process step is completed).
The shipping HU labels, and the HU content lists are printed. Warehouse operator will further put the shipping labels on the boxes. The WOs for staging are created.
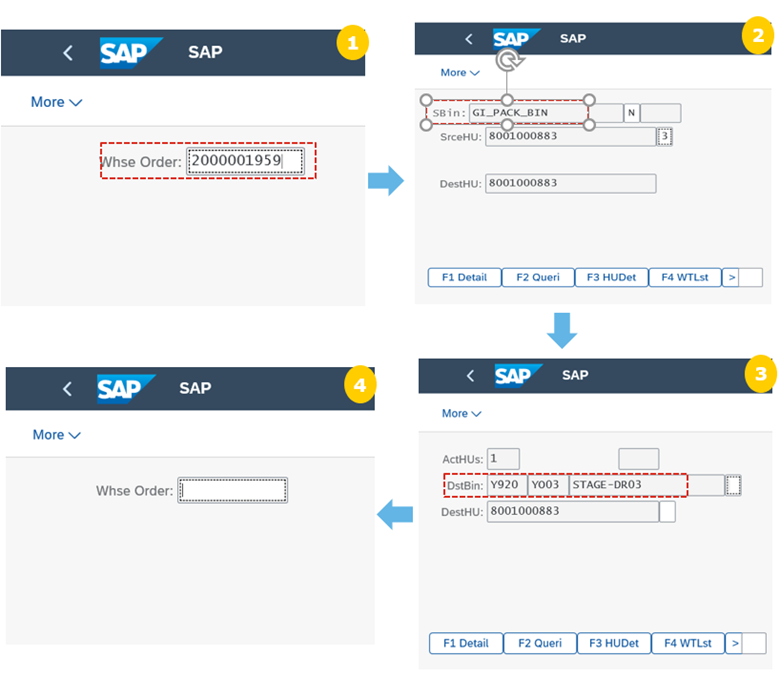
Step 7: Perform the staging process with RFUI, warehouse operator performs the staging of shipping HUs to multiple staging areas.
The warehouse worker chooses the equipment necessary for the staging (for example, a vehicle and an RF device) and logs on as a resource. The worker picks a shipping HU from the packing station and scans its ID. The system automatically finds the open HU WT created upon completion of the shipping HU. The worker is prompted to bring the shipping HU to a staging area. The shipping HUs are dropped and user scans the staging bin, thus confirming the HU WT. User drives back to the packing station to proceed with the next shipping HU.
Step 8: Post the arrival of Truck at the door. This activity is carried out in the EWM system to synchronize the trailer physical arrival at the door and in the system as well.
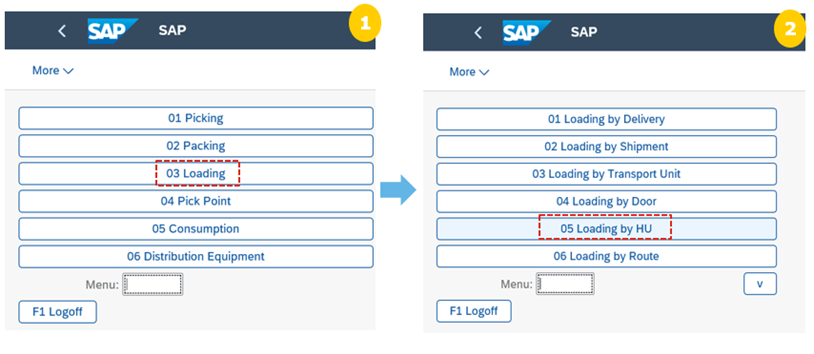
Step 9: Load the trailer. With RFUI, warehouse operator performs loading of HUs into the TUs
The warehouse worker picks a shipping HU from the staging area and scans its ID. The warehouse worker loads the shipping HU onto the truck and scans the door bin. The system automatically creates a WT for loading the TU assigned to this door and confirms it in the same step. The warehouse worker proceeds with the next shipping HU until the staging area is empty. The shipping office clerk checks that all delivery items have been loaded onto the truck and confirms the completion of the loading.
If the warehouse worker loads a HU that is designated for a different route than the route of the TU, user is notified by the system and can reverse the loading, if necessary.
Loading creates HU WTs from the staging area to the door of the outbound delivery item. Confirmation of any WT to a door bin is defined as loading WT and creates a document flow entry in the delivery order items and a status on the HU.
Step 10: Once loading is successfully completed, the shipper posts the goods issue, print the delivery notes with Bill of Lading.
The shipping office clerk posts the GI for the TU. This triggers the printing of the delivery note for each delivery and the road waybill for the TU.
The shipping office clerk hands over the delivery notes and road waybill to the truck driver.
The goods issue is sent to SAP S/4 HANA system where the billing can begin and an advanced shipping notification (ASN) can be sent to the customer.
The truck leaves the door and the premises. The shipping office clerk confirms the departure of the truck from the checkpoint and, therefore, from the door. This step is necessary for the checkpoint clerk to see that the door is free. This ends the complete process.
All testing is conducted in S/4 HANA 2020 Embedded EWM
Summary
So in summary, waves are the grouping of warehouse request items and In EWM, you can group the warehouse request items (such as the ODO items) into waves to manage the process and optimize the warehouse processing. The items assigned to a wave are generally similar in some respect, whether they are picked from a similar area or are picked in a similar way due to their size or shape, for example. The items of the wave are also generally processed together, beginning with the release of the wave and the resulting creation of the warehouse tasks and warehouse order.You can therefore use the waves to manage the timing of the processing in the warehouse.