Anthony Cecchini is the President and CTO of Information Technology Partners (ITP), an ERP technology consulting company headquartered now in Virginia, with offices in Herndon. ITP offers comprehensive planning, resource allocation, implementation, upgrade, and training assistance to companies. Anthony has over 20 years of experience in SAP business process analysis and SAP systems integration. ITP is a Silver Partner with SAP, as well as an Appian, Pegasystems, and UIPath Low-code and RPA Value Added Service Partner. You can reach him at [email protected].
Anthony Cecchini is the President and CTO of Information Technology Partners (ITP), an ERP technology consulting company headquartered now in Virginia, with offices in Herndon. ITP offers comprehensive planning, resource allocation, implementation, upgrade, and training assistance to companies. Anthony has over 20 years of experience in SAP business process analysis and SAP systems integration. ITP is a Silver Partner with SAP, as well as an Appian, Pegasystems, and UIPath Low-code and RPA Value Added Service Partner. You can reach him at [email protected].
RPA tools were unveiled in the 2000s. The predecessors of the current RPA tools were spot solutions like those from the SAP-acquired Contextor. These tools focused on automating limited sets of repetitive tasks with industry-specific solutions. In 2015, RPA became mainstream with its platforms becoming generic and broad to target the automation of most business tasks. The most common tasks handled by RPA are back-office responsibilities like billing, accounting reconciliation, ERP data entry, financial analysis and order processing.
For an RPA 101 primer, check out our blog SAP Intelligent RPA Explained.
Since the investment was made into RPA, different trends have continued defining this technology. It has, for instance, become one of the essential ones among business technology platforms. By 2021, it was estimated that 90% of midsize and large businesses would be using RPA. Unlike other business technology platforms, RPA solutions need minimal to no process changes to increase productivity and can be configured by employees without extensive programming skills.
Nonetheless, the trend currently defining the RPA landscape is low code/no-code {LCNC} RPA. Below are some facts to help you understand what this entails and means for your business.
Though RPA bots can manipulate the structured data in your application silos and databases, they can also handle unstructured data like text, speech and images usually sent from mobile devices. There is so much that your organization can achieve by combining RPA bots that will interact with the applications in your information system with an extensive range of AI technologies that will manipulate your unstructured data and simplify user interactions with chatbots. This is exactly what you are getting with intelligent RPA.
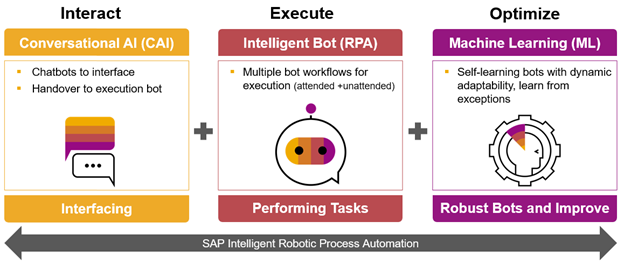
The launch of SAP’s Intelligent RPA 1.0 happened in mid-2018. Like most RPA solutions, this required a programming process that was time-consuming and needed a lot of expertise. The following are some drawbacks that companies had to deal with:
- Programming was often outsourced to systems integrators, niche RPA implementation agencies and consulting companies.
- There were long debugging and programming phases.
- Companies had to reprogram automation with each process change, something that had to be done by a limited number of trained personnel or outsourced resources.
The above drawbacks heralded the introduction of RPA solutions with a reduced or negated need for coding. This is the low code, no code (LCNC) RPA.
The concept of LCNC is not entirely new. There have been several rapid app development tools over the years that give developers access to basic platforms that are easy to use and quickly adapt to the rapidly changing technology requirements. SAP intelligent RPA 2.0 is now here and included in all S/4HANA cloud subscriptions from January 2021.
There are two main benefits of an LCNC approach for RPA including:
- Developers can work more efficiently and faster because they can focus their resources on creative, value-added tasks.
- Non-developers are empowered to build applications and extensions on their own. In so doing, they gain a flexibility level that allows them to respond to fast-changing environments according to their needs.
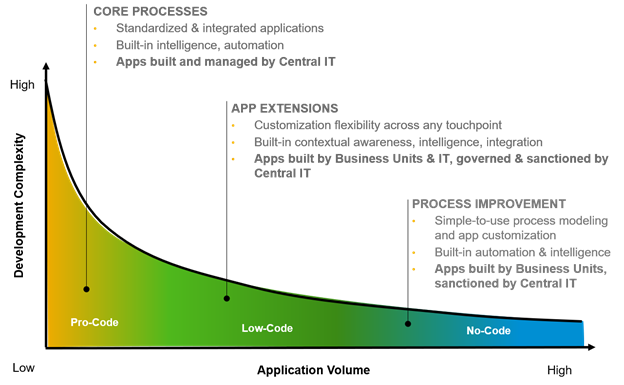
LCNC development platforms are visual software development environments allowing citizen and enterprise developers to drag and drop application components. These components are then connected to create different applications. Most people erroneously think that low and no-code platforms are similar since they are often used together.
Low-code tools require their users to have some level of coding knowledge though less than what you need with traditional app development. The tools are generally used by professional developers to help them handle complex unique work that has more value for companies. Those without programming knowledge can also use the tools to expand the functions in an app or develop simple apps. Low-code tools are used for tactical apps and those that handle crucial processes for your company, such as digital transformation initiatives.
No-code tools target people with no programming or coding knowledge, but who want to understand the rules and needs of their business apps. These tools allow users to quickly and easily build, test then deploy their business apps so long as the tools will align with their commodity functions. No-code tools are often used for tactical apps that handle simple functions.
These differences are summarized in the diagram below:
The focus on LCNC by SAP presents the company with an opportunity to extend its reach beyond software developers to everyone in business. The goal of SAP in LCNC RPA is to:
- Democratize IT development such that everyone can easily compose processes and applications. In so doing, there are many people to drive digital transformation initiatives.
- Enable transparency, synergy and governance between business and IT units.
- Deliver a single platform that accelerates data integration while easing application extension development to achieve data-to-value. The single platform also enables hyperautomation. This is the seamless integration Of Business Process Management, Analytics, RPA, Application Extensions and Process Insights.
Visual design of bot-enabled workflows
- Develop bots with a step-by-step sequence and set of dependencies
- Attach trigger mechanisms for attended or scheduled autonomous bots
- Apply APIs and machine-learning services to make bots intelligent
Repository for bot skills and analytics
- Tap into a container of automation steps that can be reused for bot development
- Publish or consume available RPA bots that meet your business needs
- Analyze bot-operation statistics and expedite process execution history
Rich content offering of pre-built automations
- Ready-to-use bots to quickly solve your business challenges
- Learning and best practices content to get you started free of charge
- Content directly available from cloud tenants within minutes
There are several benefits of investing in Intelligent RPA 2.0…
Accurate processing throughout: With RPA 2.0, the robots on servers do not need humans to initiate their processes. As such, they will not be limited to regular work times. This is a huge benefit for your customer service department where you are sure that clients will have their queries immediately answered throughout. Moreover, the results of the robots are generally more accurate than those of humans that are prone to errors when people get tired.
Scalability: Implementing intelligent RPA 2.0 introduces high levels of flexibility that allow you to process more queries and quickly adapt to changes. This will eliminate overworking, more so in businesses that have seasons when they handle a lot of work. The scalability also makes RPA 2.0 your best choice if you frequently change processes because people can focus on modifying robots rather than remembering processes.
Ease of managing business processes: The statistics from RPA 2.0 bots can be processed then used to better understand business processes and know how best to improve them. With an understanding of your business processes, you will also know what to change to maximize client satisfaction.
Reduced operation costs: Implementing the automation of tedious and repetitive tasks allows faster handling while reducing your labor costs. This translates to reduced operating costs and increased profits.
Improved work quality
Summary
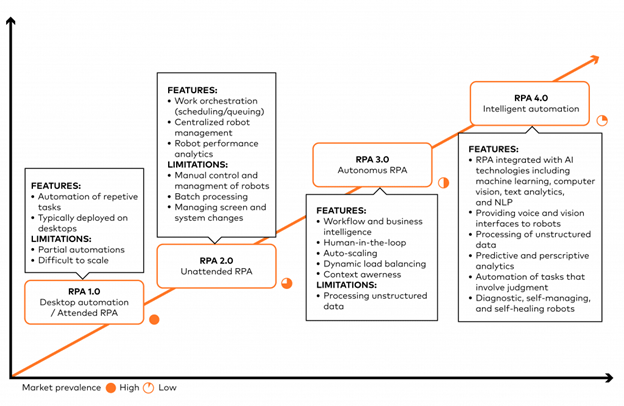
Intelligent RPA is not stopping at RPA 2.0. Thanks to artificial intelligence, robots will become increasingly independent of human input in the future. The expected stages of intelligent RPA are RPA 3.0 {autonomous robots} and RPA 4.0 {cognitive robots} in which robots will harness the full advantages of artificial intelligence. Here is a diagram of what you can expect in the future of intelligent RPA.